基金项目:国家自然科学基金(11802219)
作者简介:姜 薇(1987—),女,博士,工程师,研究领域为液体火箭发动机强度
(1.液体火箭发动机技术重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710100;2.西北工业大学 航空学院, 陕西 西安 710072)
(1.Science and Technology on Liquid Rocket Engines Laboratory, Xi'an 710100;2.School of Aeronautics,Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710072)
ductile multiple-crack; cell; void coalescence; plastic limit-load
拉伸载荷作用下,裂尖附近具有较高的应力三轴度,微孔洞体积扩张及随后内部韧带颈缩是主导韧性裂纹扩展的细观机制。为基于微孔洞损伤机制模拟裂纹扩展,需要建立合理的孔洞贯通准则。基于三维体胞分析,建立了2524-T3铝合金的宏观等效应变失效准则。通过假设孔洞在贯通前保持球形扩张,将塑性极限载荷准则推导为仅依赖于宏观应变的形式。这两种准则分别与Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman(GTN)模型结合在一起,形成了GTN-E及GTN-L模型,对2524-T3铝合金薄板中的韧性多裂纹扩展过程进行了模拟。模拟结果与试验结果的对比表明,可以有效地分析韧性多裂纹的扩展连通过程。
For the pre-cracked specimen under tensile loading, due to the high stress triaxiality ratio near the crack tip, microvoid dilation and subsequent coalescence by reduction of the inter-void ligament dominates the failure mechanism.Void coalescence criteria should be established properly to simulate the crack extension based on the void damage mechanism.Firstly, the results of 3D cell computation were used to establish a macroscopic equivalent strain criterion for 2524-T3 aluminum alloy.Thereafter, a new form of the plastic limit-load criterion only depending on macroscopic strain is derived with the assumption that voids keep the spherical expansion until coalescence.Finally, these two void coalescence criteria are combined with Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman(GTN)model to form GTN-E and GTN-L models, respectively.The ductile multiple-crack extension process in 2524-T3 aluminum alloy sheet was simulated.Comparison vith the test results shows that the predictions of the fracture behaviors, including crack extension, coalescence and final fracture, have a good agreement with the experiment data, which also validates the current approach.
准确模拟金属的韧性断裂行为已经成为工程实践中越来越迫切的需求,尤其是对复杂结构进行可靠性评估和结构优化设计时。细观损伤力学从材料内部细观缺陷的演化过程揭示裂纹起裂、扩展直至断裂的原因,建立基于机制的损伤模型,是准确预测韧性断裂最有潜力的方法之一。细观层面,韧性断裂通常是材料内部微孔洞的形核、扩张、变形及相互贯通一系列行为不断积累的结果。韧性金属在外部载荷作用下会表现出两种依赖于应力状态的破坏机理[1-3]。高应力三轴度下,孔洞体积扩张及随后的韧带颈缩逐渐抵消基体的应变强化作用,使材料性能弱化并在孔洞大面积贯通后迅速丧失承载能力,称为内部韧带颈缩机制(inner-necking mechanism)。低应力三轴度下,孔洞形状会改变,表现为孔洞的旋转、扭曲等,称为孔洞剪切机理(void shearing mechanism)。
经典GTN(Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman)[4-5]模型考虑了完整的微孔洞萌生、长大及贯通过程,能较好地预测中到高应力三轴度下的韧性断裂过程。该模型近年来得到了极大的发展和广泛的应用, Kim 等(2007)[6]借助于微孔洞细观损伤模型分析了2024-T3铝合金中的韧性断裂过程; Nahshon和Hutchinson(2008)[7-8]对GTN模型进行了扩展,使之适用于剪切主导的应力状态; Jiang 等(2016)[2]基于GTN模型提出了一种适用于高、中、低甚至负应力三轴度的新模型,可以模拟拉、压、剪等多种载荷形式下的韧性破坏过程。但是,从光滑试样得到的材料参数常常不能准确预报裂纹试样的破坏。这是由于初始完好的试样与裂纹试样在载荷作用下,应力状态具有极大的差异。应用Needleman和Tvergaard[5]的双线性孔洞贯通模型时,临界孔洞体积分数(fc)——作为材料内部孔洞开始贯通的标志(即材料宏观失效的起点)常被视作仅与材料相关的常数。然而许多研究都表明临界孔洞体积分数与应力状态、初始孔洞体积分数、孔洞形状、孔洞间距以及基体应变强化指数等因素密切相关[8-10]。因而有必要针对含初始裂纹结构的韧性断裂问题,建立能够考虑材料细观结构特征和应力状态影响的孔洞贯通准则。
本文针对最常见的拉伸型裂纹,基于体胞计算结果建立了临界宏观等效应变失效准则,并确定出适合2524-T3铝合金的参数。采用建立的准则以及Thomason的塑性极限载荷准则[12-13]对GTN模型进行扩充,提出了新的多孔质塑性损伤模型——GTN-E模型(以临界宏观等效应变准则作为孔洞贯通条件的GTN模型)和GTN-L模型(以塑性极限载荷准则作为孔洞贯通条件的GTN模型)。在这两个模型中,孔洞贯通的起点不再被看作材料常数,而是分别由临界宏观等效应变准则和塑性极限载荷准则自动确定。最后,对2524-T3铝合金薄板中的韧性多裂纹扩展过程进行模拟分析。
Gurson理论假设材料由基体和微孔洞两部分组成,屈服面由等效应力、静水应力以及损伤变量(孔洞体积分数,f)共同决定。GTN屈服函数具有以下形式[4-5]
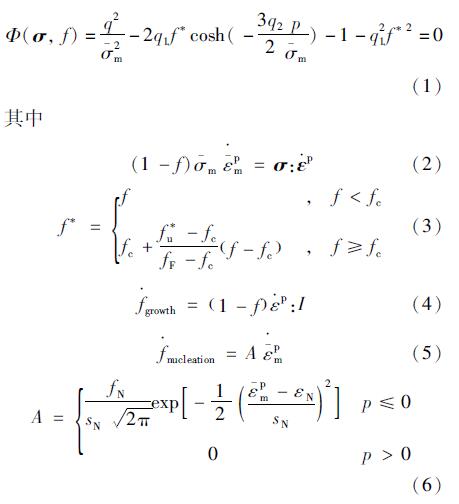
式中:σ为应力张量; f为当前孔洞体积分数; q为等效应力; p为静水应力; q1,q2为常数; σ-m为基体材料的流动应力,基体材料的应变强化作用由σ-m=σ-m(ε-pm)引入; ε-pm为基体等效塑性应变,可由材料的塑性功,即式(2)确定; ε·p为塑性应变率张量; f*为函数,用来考虑孔洞的贯通作用; fc为贯通开始时的临界孔洞体积分数; fF为材料最终失效时的孔洞体积分数; f*u=1/q1为应力零时的f*的值,载荷作用下,孔洞体积分数的改变主要源于现有孔洞的长大以及新孔洞的萌生; f·growth为现有孔洞长大引起的孔洞体积分数改变,与塑性体积改变有关,由式(4)给出; f·nucleation为新孔洞萌生引起孔洞体积分数的改变,新孔洞萌生的主要形式是基体粒子在界面处断裂或脱粘,可采用应变控制的孔洞萌生模型来描述,由式(5)给出; A为孔洞萌生强度因子,是基体等效塑性应变ε-pm的函数,通常认为只有在拉伸静水应力的作用下孔洞才会萌生,且服从式(6)给出的正态分布形式; fN为孔洞体积分数中形核部分的极限值; εN为孔洞萌生时的平均等效塑性应变; sN为该正态分布的标准差。
采用均匀化思想,连续材料可近似看作由大量中心含孔洞的立方体代表性体积元RVE(representative volume element),或称为体胞元(cell)紧密堆积构成,如图1(a)所示。大粒子或夹杂的平均距离被看作体胞的边长。含裂纹体中,假设裂纹尖端前方分布着一层这样的体胞,受高应力三轴度和高塑性应变双重作用,靠近裂尖的孔洞会率先长大,达到临界状态后,裂尖与孔洞之间的韧带丧失承载力,发生颈缩进而二者连通,裂纹向前扩展。于是,考虑采用三维体胞计算得到的表征体胞韧带颈缩失效的临界宏观等效应变作为孔洞开始贯通(材料宏观开始失效)的标志,结合GTN模型模拟裂纹扩展。
进行体胞分析时,采用精细有限元网格模拟出一个含孔洞体胞的真实形状,施加周期性边界条件,分析孔洞在弹塑性基体中的变形历程以及相关的细观力学行为; 体胞内任意材料点上的细观应力、应变状态分别用张量σ和ε表示,作用在体胞边界上的宏观应力、应变张量记作Σ和E,如图1(b)所示。为满足体胞元在宏观材料中周期性分布的假设,需要施加边界使体胞变形后的外表面保持平面且始终平行于初始外表面。为研究应力状态的影响,还需要使体胞的宏观应力三轴度(T)和Lode应力参数(μ)在变形中保持恒定,不受大变形以及变形中刚度为负等因素的影响。这可以通过以下过程实现:①预先给定宏观主应力Σ3和一个确定的应力状态(T,μ),解出相应的主应力比ψ1和ψ2; ②体胞按照给定的主应力比加载,采用ABAQUS/Standard中的Riks分析步进行计算
T=(Σm)/(Σe)(7)
μ=(2Σ2-Σ1-Σ3)/(Σ1-Σ3)=-cos(3θ)=-(27J3)/(2Σe)(8)
ψ1=(Σ1)/(Σ3)=(1.5T-cos(θ-π/3))/(cos(θ)+1.5T)(9)
ψ2=(Σ2)/(Σ3)=(1.5T-cos(θ+π/3))/(cos(θ)+1.5T)(10)
式中:Σ1,Σ2,Σ3为宏观主应力; Σm为宏观平均应力; Σe为宏观等效应力; θ为罗德角。变形中任意时刻的孔洞体积分数可以由解析公式[10]计算得
f=1-(V0(1-f0))/V-(ΔVelastic)/V(11)
其中
ΔVelastic=V0(1-f0)(3(1-2ν))/EΣm(12)
式中:ΔVelastic为弹性静水应力引起的体胞体积改变; ν为泊松比; E为弹性模量; V0为初始体胞体积; V为当前体胞体积。
为建立宏观等效应变准则,采用三维立方体胞模型,对2524-T3铝合金进行了细观力学分析。本文研究对象为拉伸载荷下的含裂纹体,裂纹尖端附近的材料处于高应力三轴度状态,此时Lode角对韧性断裂的影响很小。因而,这里考虑不同应力状态时,只对应力三轴度 T 进行了区分,Lode角参数仅考虑 μ=-1(单轴拉伸或双轴压缩)的情况。预先采用有限元方法对本文各组试件在不同裂纹长度时裂尖前方单元的应力三轴度水平进行了试计算,确定出裂纹扩展过程中 T 的范围在1~2之间。因此,计算中考虑了T=1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8 和2,共6种应力状态。初始孔洞体积分数 f0 考虑了1.77*10-3,4.19*10-3,8.18*10-3 和 1.41*10-2的四种情况。
体胞分析结果显示:高应力三轴度下,临界孔洞体积分数 fc和临界宏观等效应变E-c均依赖于应力三轴度和初始孔洞体积分数。其中,E-c更适合作为表征体胞失效的指标,因为E-c对应力三轴度和初始孔洞体积分数的依赖都清晰地表现为负指数关系,便于建立准则。考虑采用体胞分析结果建立如下的临界宏观等效应变准则,作为孔洞贯通的起点
E-c=E-c(f0,Tave)(13)
式中Tave为材料点经历的平均应力三轴度水平,由下式计算
Tave=1/(E-f)∫E-f0(Σm)/(Σe)dE-(14)
式中E-为当前宏观等效应变。应用该准则时,当由GTN屈服面计算的宏观等效应变达到式(13)给出的临界值时,令当前孔洞体积分数即为fc,并认为孔洞开始贯通。
图2(a)是计算得到的4种初始孔洞体积分数的2524-T3铝合金在拉伸载荷下的临界等效应变随应力三轴度的变化。基于图2(a)中的结果建立 2524-T3 铝合金材料的失效准则时,采用如下的方法:①将图2(a)中计算得到的24个临界宏观等效应变E-c分为6组,每种应力状态下的4个值拟合为E-c对初始孔洞体积分数f0的负指数关系,拟合函数采用含有3个参数指数关系:E-c=aebf0+c,其中,a,b,c为拟合参数,得到图2(a)中的6条实曲线; ②采用试验或者数值的方法确定出材料的初始孔洞体积分数(确定出本文材料的 f0 为0.005); ③在图2(a)中以f0=0.005的直线在拟合得到的6条曲线上截取出对应于各应力状态下的E-c; ④将得到的f0为0.005时的各应力状态下的E-c拟合为应力三轴度的负指数函数,即得到了适合本文2524-T3 铝合金在高应力三轴度(T=1~2)下的宏观等效应变准则
E-c=3.384e-1.907Tave+0.127(15)
图2(b)给出了上述准则以及体胞计算直接得到4种初始孔洞体积分数体胞的结果。将与宏观等效应变失效准则相结合的GTN模型称为GTN-E模型。
韧性断裂机理研究表明,孔洞贯通是塑性应变在孔洞间韧带上局部化带来的瞬间塑性失稳过程。Thomason(1985)[12]研究发现:拉伸主导的韧性断裂过程中,当材料内部孔洞间的韧带不能支撑由当前应力、应变场分配的等效载荷时,会发生内部颈缩并引起孔洞贯通。换言之,孔洞结束均匀长大,体胞丧失稳定的塑性变形,可以看作是孔洞开始贯通的标志。这一临界状态可以由内部韧带达到塑性极限载荷(plastic limit-load)来表征,Thomason的孔洞贯通条件可以表示为
σ1=σLoc1(16)
式中:σ1为宏观材料点在当前状态下的最大主应力; σLoc1为细观尺度上,含孔洞体胞能够承受塑性载荷的极限,强烈地依赖于孔洞和体胞的几何尺寸。塑性变形初期,孔洞尺寸很小,相应的σLoc1很大; 随着孔洞的长大,σLoc1逐渐减小。考虑中心含球形孔洞的三维体胞,初始是边长为2L的立方体,受z向拉力后在3个方向的边长分别为2Lx,2Ly,2Lz。孔洞是初始半径为R的球体,受z向拉力后成为在3个方向的半轴长分别为Rx, Ry, Rz的椭球体。Thomason给出该体胞在单轴拉应力作用下失稳的条件为
(σLoc1)/(σ-m)=[1-(π)/4((Rx)/(Lx))2][α((Rz)/(Lx-Rx))-2+β((Rx)/(Lx))-1/2](17)
式中系数a和b与应变强化指数n有关。式(17)给出的塑性极限载荷形式,含有体胞和孔洞的几何特征参数,不便与GTN模型等多孔塑性损伤本构结合使用。
体胞分析结果表明:高应力三轴度时,初始为球形的孔洞在变形过程中基本能够保持球形,但体积会明显地长大。假设孔洞在贯通前的变形过程中严格保持球体,由式(17)给出的塑性极限载荷准则经过如下数学推导可变形为仅含宏观等效应变的形式,方便地作为判断孔洞贯通开始标志。受z方向单轴拉伸的含孔洞立方体体胞,在x, y, z三个方向上的宏观应变为
Ex=ln((Lx)/L), Ey=ln((Ly)/L), Ez=ln((Lz)/L)(18)
于是,变形历程中任意时刻体胞的体积变化率可以表示为
V/(V0)=exp(Ex+Ey+Ez)(19)
式中V0和V分别是体胞在初始和当前时刻的体积。于是,当前的孔洞体积可以表示为
Vvoid=fV0exp(Ex+Ey+Ez)(20)
变形过程中,孔洞平均半径为
Rave=[3/(4π)f(2L)3exp(Ex+Ey+Ez)]1/3(21)
同理可得
Lx=Ly=[L2exp(Ex+Ey)]1/2(22)
定义几何因子χ为孔洞直径与体胞边长的比值,由式(21)和式(22)可得
χ=(Rave)/(Lx)=([3/(4π)fexp(Ex+Ey+Ez)]1/3)/([exp(Ex+Ey)]1/2/2)(23)
若假设孔洞在贯通前的变形中始终保持球形(Rx=Ry=Rz),则式(17)可以变形为
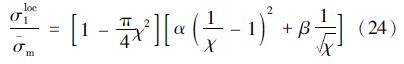
式中的几何因子χ由当前应变确定。采用塑性极限载荷准则结合GTN模型预测韧性断裂时,由GTN屈服函数给出的某一材料点的最大主应力s1达到由式(24)确定的σloc1,孔洞开始贯通,在GTN屈服函数中采用f*代替f。将与塑性极限载荷准则相结合的GTN模型称为GTN-L模型。
所有试件板长220 mm,宽50 mm,厚1.6 mm,分别考虑了一条、两条和四条孔边裂纹的情况,如图3所示。每件试样在长度对称截面上开两个直径为4 mm的圆孔,左侧为1号孔,右侧为2号孔。两孔圆心间距24 mm,圆心距离板边均为13 mm。W50-1和W50-2组试件在1号孔右侧及2号孔左侧预制裂纹,初始裂纹长度见表1。W50-3组试件在1号孔和2号孔的左右两侧均预制裂纹,初始裂纹长度见表2。W50-4组和W50-5组仅在1号孔的右侧预制裂纹,初始裂纹长度见表3。
经测定,2524-T3铝合金的拉伸性能常数为:杨氏模量E=68GPa,泊松比ν=0.33,初始屈服强度σ0=306.8 MPa。采用Ramberg-Osgood形式拟合拉伸性能试验中获得的真实应力-塑性应变曲线
(εp)/(ε0)+1=α((σ)/(σ0))n(25)
式中:拟合参数α=1.804; n=8.765。
图4(a)将采用GTN-L和GTN-E损伤模型模拟
W50-1和W50-2组试件裂纹扩展过程得到的载荷-位移曲线与试验数据进行了对比。两组试件在达到各自最大载荷之后,载荷明显下降,但并未完全丧失承载能力。这是因为中心裂纹连通后,截面未断部分继续承载,随后载荷会有短暂上升,当连通后的长裂纹再次向前扩展时载荷随之下降,继而试件完全断裂。GTN-L和GTN-E损伤模型均模拟出了载荷-位移曲线的这一变化过程。图4(b)为试验与计算得到的W50-3试件的载荷-位移曲线,两种损伤模型均给出了与试验结果基本一致的预测:试件在达到最大载荷后迅速被拉断。图4(c)是试验和两种损伤模型计算得到的W50-4和W50-5试件的载荷-位移曲线。在预制裂纹过程中,W50-5试件由于需要在1号孔右侧预制较长的疲劳裂纹,1号孔左侧也在疲劳载荷作用下出现了初始裂纹,计算中初始裂纹取为实际预制的裂纹长度。GTN-L和GTN-E损伤模型给出了与试验结果基本一致的载荷-位移曲线。W50-4试件中,裂纹首先在两孔之间连通形成1条较长的中心裂纹,然后试件被迅速拉断; W50-5 试件中,1号孔右侧裂纹在孔间韧带上扩展的同时,1号孔左侧的疲劳裂纹亦扩展至试件左侧边缘,形成一条较长的边裂纹后试件被迅速拉断。
图5给出了采用GTN-E模型计算得到的W50-3 试件的裂纹连通过程。由图5(a)可知:a1 和 a2裂纹在夹持端位移达到1.3 mm时开始扩展,1.8 mm时连通; a3 和 a4裂纹在夹持端位移达到1.4 mm时开始扩展,进而试件在夹持端位移为1.9 mm彻底拉断。
由图5(b)可知:a1和a2裂纹在载荷达到18.03 kN后开始扩展,a3和a4裂纹在载荷达到18.16 kN后开始扩展; 随后的短暂扩展中由于应变强化作用载荷会小幅上升,达到最大值18.30 kN后载荷随裂纹扩展迅速下降,a1 和 a2 裂纹连通时载荷下降至11.93 kN。
采用两种考虑应力状态和细观结构特征影响的孔洞贯通准则——临界宏观等效应变准则和塑性极限载荷准则对经典Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman(GTN)模型进行了扩充,建立了能够准确预测裂纹试样韧性断裂过程的GTN-E和GTN-L损伤模型。采用GTN-E和GTN-L损伤模型对不同初始裂纹形式的2524-T3铝合金薄板试样中的韧性多裂纹扩展、连通过程进行了数值分析,得出以下结论:
1)将采用损伤模型计算得到的各组试样的全局载荷-位移曲线和相应试验数据进行了对比,损伤模型均给出了与试验结果相吻合的预测。
2)以W50-3组试样为代表,分析了多裂纹彼此之间的连通过程,给出了由GTN-E损伤模型计算得到的位移-裂尖位置、载荷-裂尖位置曲线。
以上结果显示本文方法可以方便有效地对含裂纹薄板的剩余强度做出合理预测。