作者简介:郭 敬(1979—),女,博士,高级工程师,研究领域为液体火箭发动机试验技术
备注
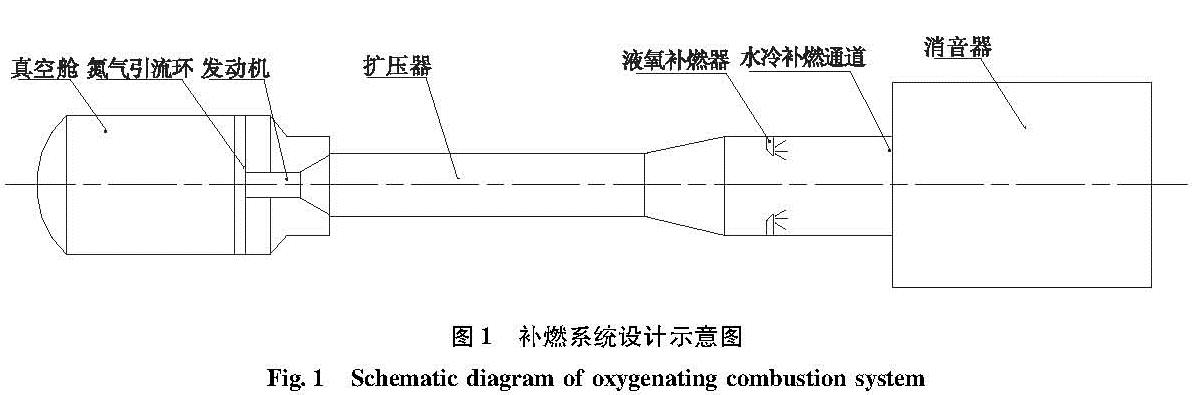
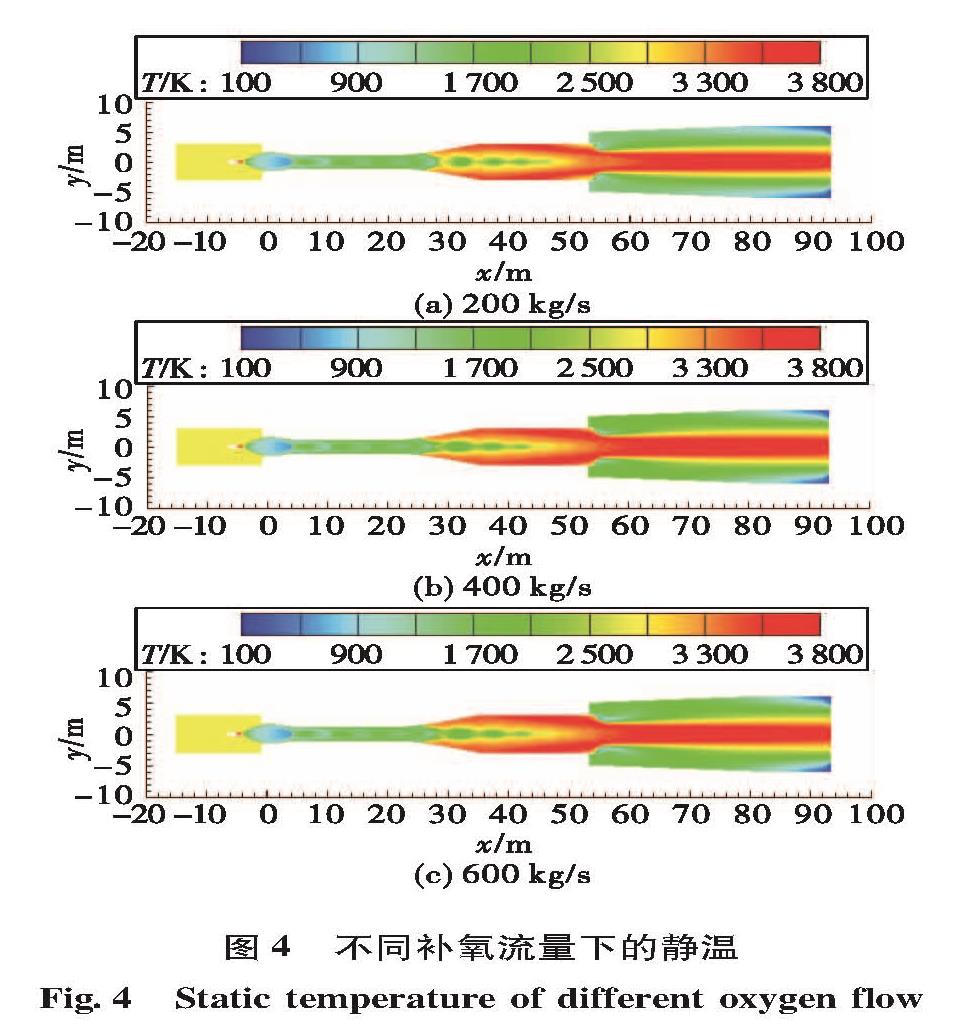
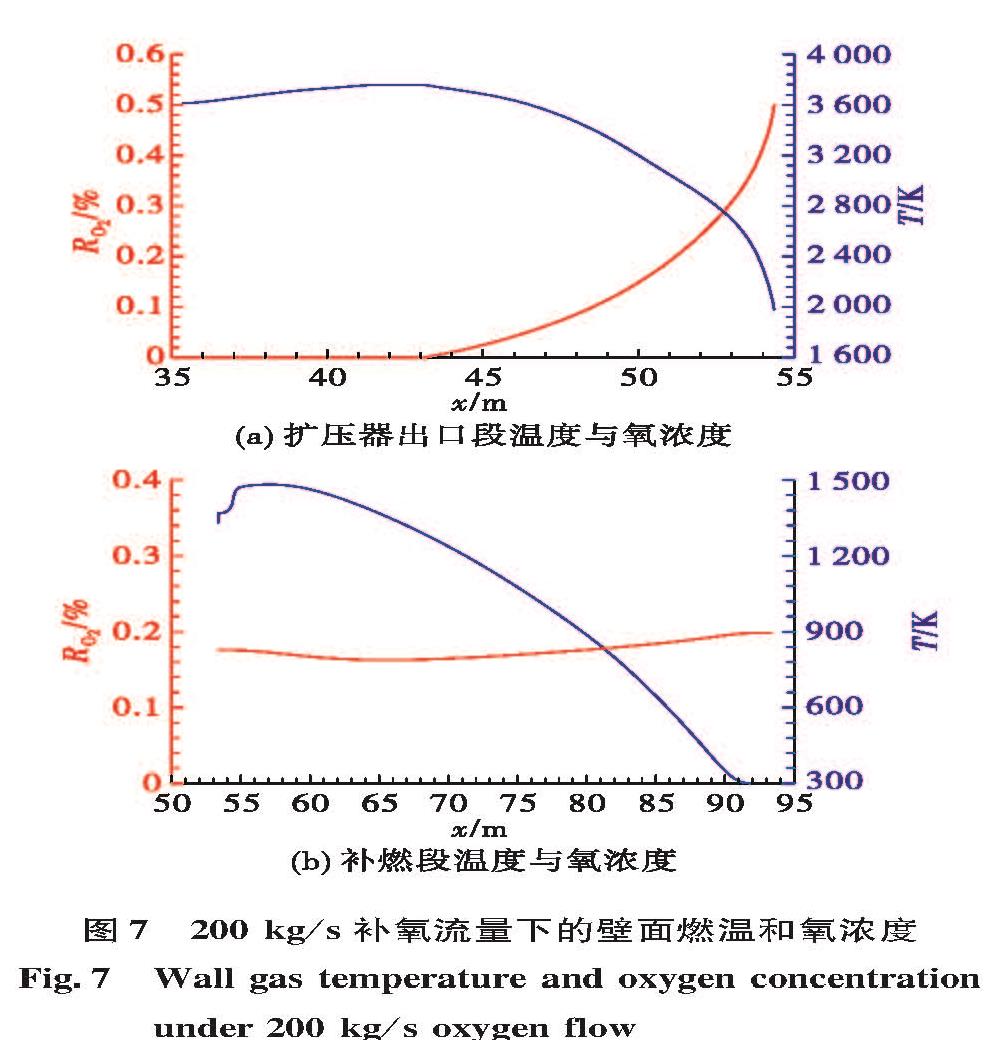
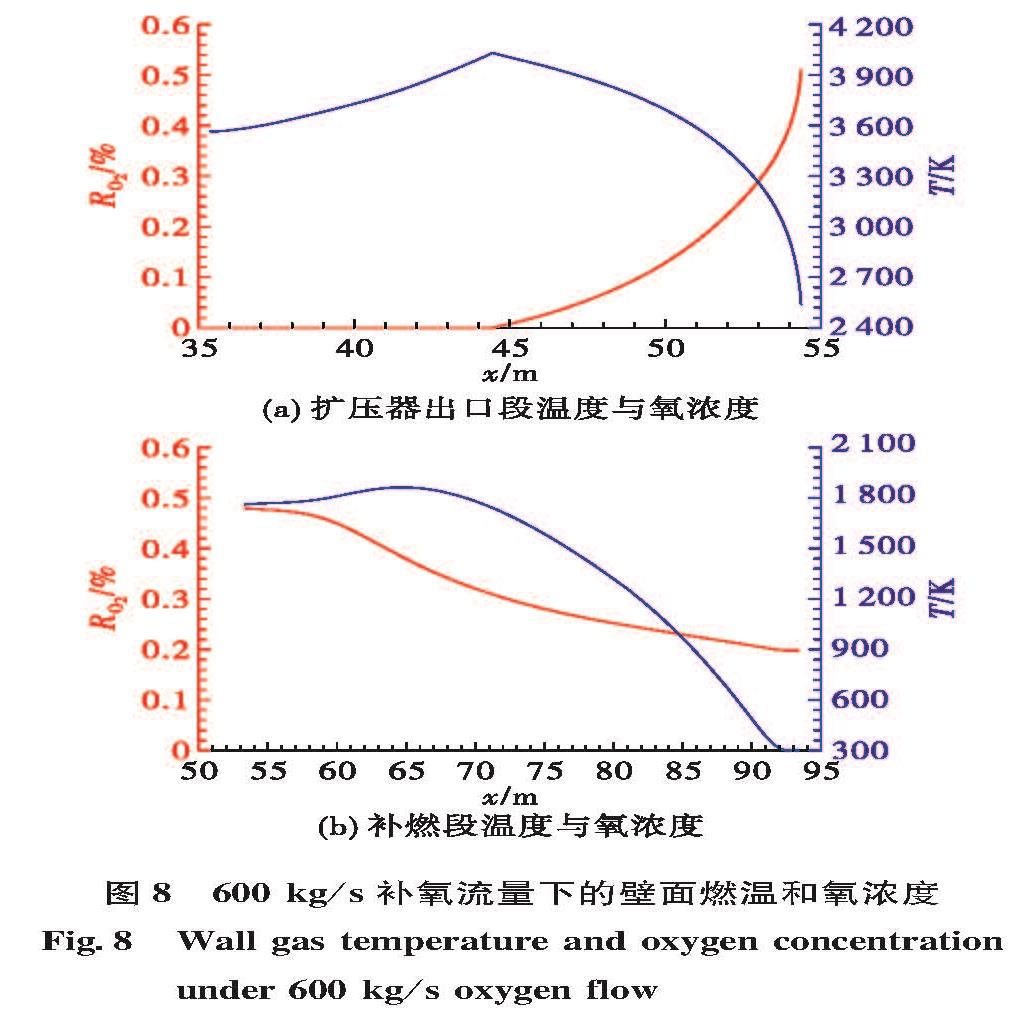
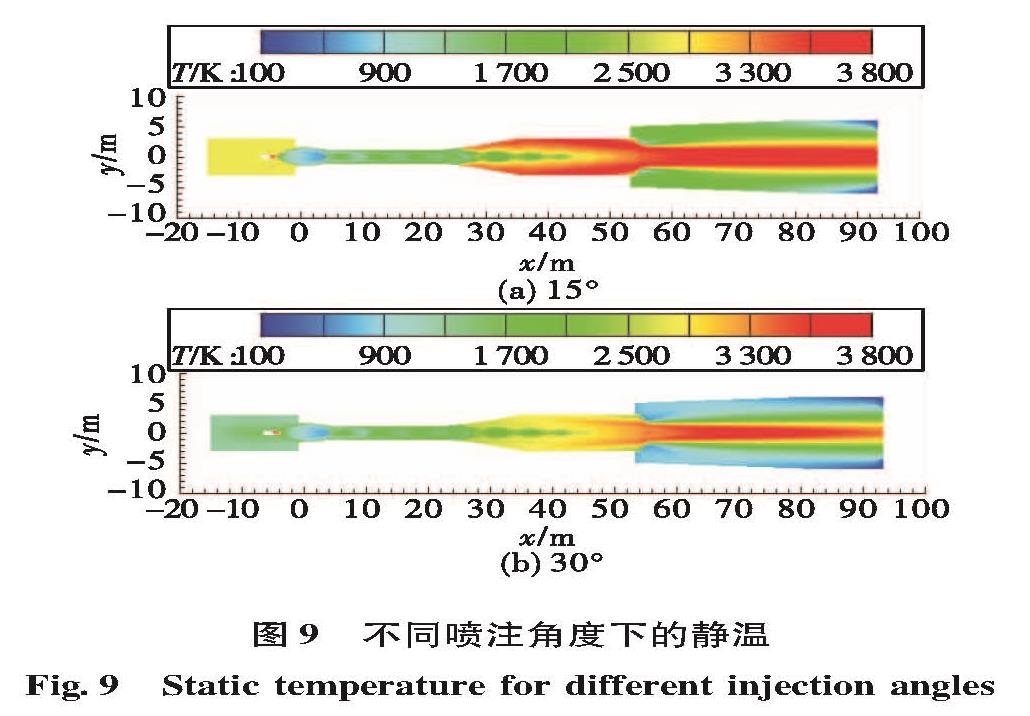
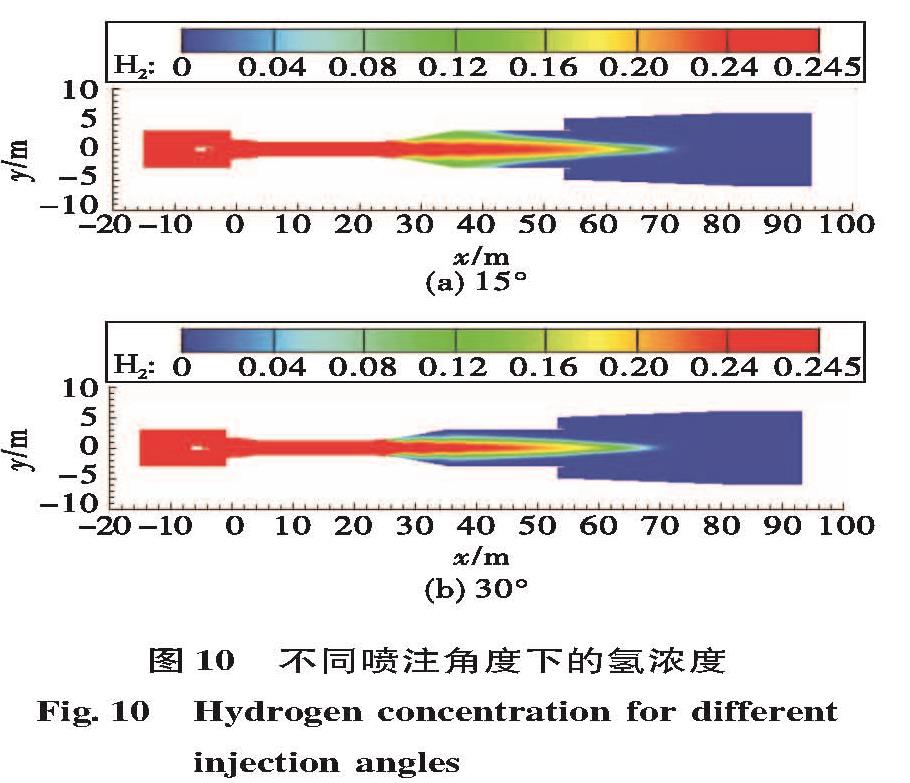
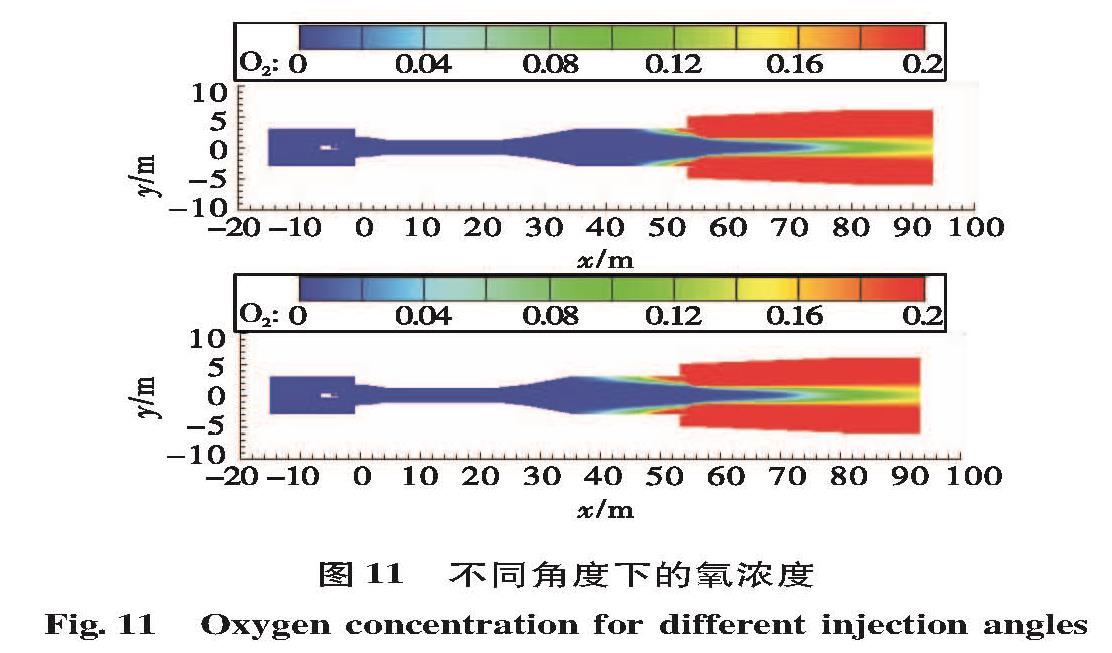
为了研究液体火箭发动机试验富燃燃气安全处理方法,确保发动机试验过程的安全,通过对未来大推力氢氧发动机高模试验关键参数设计,确定富氢燃气补氧燃烧方案,并在此基础上建立大推力氢氧发动机高模试验富氢燃气补氧燃烧仿真模型,对补氧燃烧过程进行仿真研究,研究补氧流量和液氧喷注角度对燃烧过程及高模系统的影响,以验证补氧燃烧方案的可行性。仿真结果表明补氧补燃方案可以安全处理发动机燃气中的富氢,保证高模试验安全。并且补氧量越大,燃烧长度越小,热防护难度增加; 补氧喷注角度增加对氢燃尽长度影响不大,但使设备热防护难度增大。
In order to study the safe treatment method of fuel-rich gas in liquid rocket engine test and ensure the safety of the engine test process, the hydrogen-rich gas oxygenating combustion scheme was determined based on designing the key parameters of altitude simulation test large thrust hydrogen/oxygen rocket engine in the future.For verifying the scheme feasibility, a simulation model of oxygenating combustion of altitude simulation test for the large thrust hydrogen/oxygen rocket engine was built to simulate the oxygenating combustion process, and the effects of oxygen flow and injection angle on the combustion process and altitude simulation test were studied.Simulation results show the hydrogen-rich gas combusts completely and the altitude simulation test is safe.The more the oxygen supplementation is, the shorter the combustion length is and the more difficult the thermal protection is.The increase of oxygen injection angle has little effect on the hydrogen burnout length, but it makes thermal protection of equipment more difficult.