作者简介:刘巾杰(1989—),女,硕士,工程师,研究领域为液体火箭靶场数据处理
备注
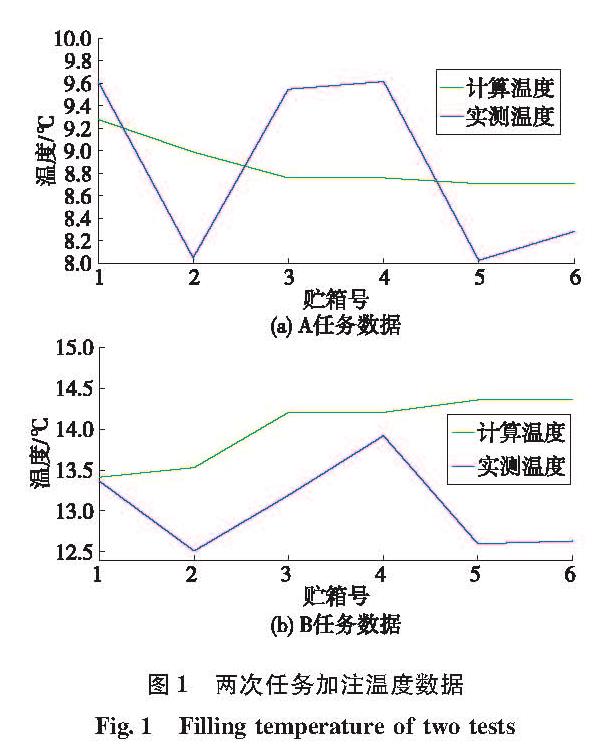
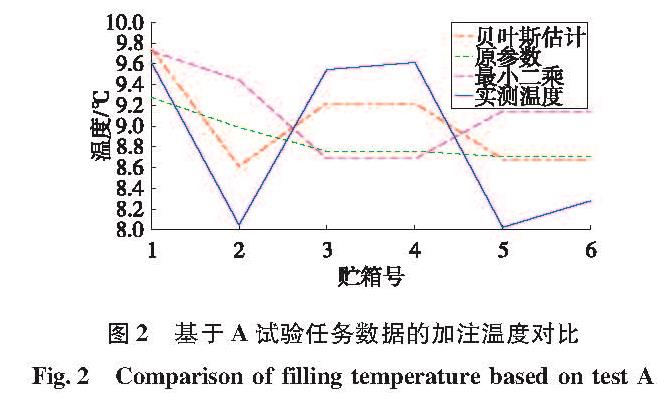
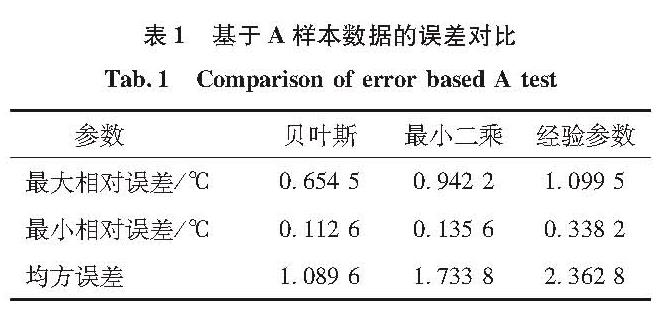
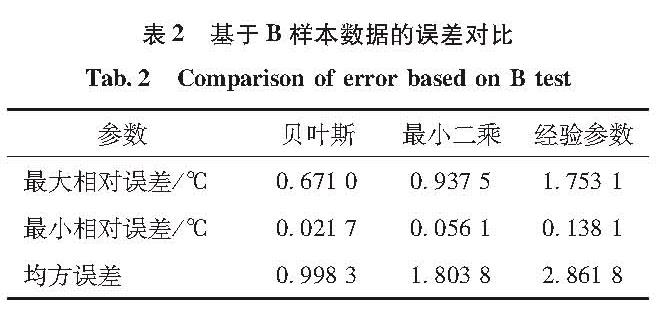
为消除火箭煤油加注实测温度与现行加注温升模型计算理论温度之间的偏差,准确估计煤油加注温升实现精确加注、精准控制,在靶场实测数据仅为小样本数据的现实条件下,采用贝叶斯回归方法,将经验参数作为先验信息给出待估参数的先验分布,由实测数据计算贝叶斯风险,通过最小化风险函数实现对煤油加注温升模型的参数优化估计。数值实验结果表明,与给定的经验参数和经典最小二乘估计参数相比,贝叶斯估计参数估算的加注结束温度与实测温度误差显著减小,且随着可用的数据样本容量相应增大,贝叶斯回归分析的参数估计精度呈现收敛趋势。贝叶斯方法进行煤油加注温升模型参数估计有效提高了加注温升模型精度,为提高推进剂加注精确度提供了方法基础。
In order to eliminate the deviation between the actual rocket's kerosene filling temperature and the theoretical result calculated by current filling temperature rise model, and estimate kerosene temperature for accurate injection and precise control, Bayesian regression method was proposed to estimate fluctuation coefficient of the temperature rise model based on a very few sample data at launching site.It takes the empirical parameters as the prior information to give a distribution of parameters to be estimated, and uses real data to calculate Bayesian risk.The parameters of the filling temperature rise model were optimized by minimizing the risk function.Numerical results show that, compared with the given experience parameters and least square results, the kerosene temperature calculated by Bayes regression is much closer to the actual result.With the increase of available data sample capacity, the parameter estimation accuracy of Bayesian regression tends to converge.Bayesian regression can improve the precision of filling temperature rise model efficiently, and provides a foundation to improve the accuracy of propellant filling.