基金项目:国家自然科学基金(51676010)
作者简介:赵娅(1995—),女,硕士,研究领域为微尺度流动与传热
(School of Astronautics, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China)
micro-nozzle; numerical simulation; flow mechanism; work performance; thermodynamic non-equilibrium phenomenon
微喷管作为微推进系统中的重要部件,其工作性能的研究对于微推进系统的设计有着重要理论指导意义。采用求解带滑移边界条件的N-S方程和直接模拟蒙特卡洛(DSMC)方法,研究微喷管中的稀薄流动,通过设定气体分子转动松弛所需要的松弛碰撞数Zrot研究微喷管中的热力学非平衡现象。结果 表明:Kn>0.1时,微喷管中流动开始变得稀薄,连续性假设失效,N-S方程求解结果出现误差; 随着微喷管中流动稀薄程度增加,热力学非平衡现象逐渐明显; 热力学非平衡现象使微喷管内气体内能转化为平动能的量减少,微喷管内速度和推力整体减小; 热力学非平衡现象对微喷管流场影响大于对其工作性能的影响,考虑转动松弛对微喷管内温度场的影响大于速度场。
As an important component in the micro-propulsion system, the study on the work performance of micro-nozzle has important theoretical guiding significance for the design of the micro-propulsion system. N-S equation with the slip boundary condition and direct simulated Monte Carlo(DSMC)method were used to study the rarefied flow in the micro-nozzle. The thermodynamic non-equilibrium phenomenon in the micro-nozzle was studied by setting the number of relaxation collision Zrot required for the rotational relaxation of the gas molecules. The results show that when Kn>0.1, the flow in the micro-nozzle begins to become rarefied, the continuity assumption fails, and the N-S equation results in errors. With the increase of the flow rarefaction in the micro-nozzle, the thermodynamic non-equilibrium phenomenon is gradually obvious. The thermodynamic non-equilibrium phenomenon reduces the amount of gas internal energy converted into translational kinetic energy in the micro-nozzle, which is followed by the velocity and thrust in the micro-nozzle decreasing. The thermodynamic non-equilibrium phenomenon has greater influence on the flow field of the micro-nozzle than on its working performance. The influence of considering the rotational relaxation on the temperature field is larger than the velocity field in the micro-nozzle.
为满足空间微小卫星和微型动能武器的工作要求,实现准确的姿态、高度控制和位置保持,需要能提供适当推力水平和推力脉冲的微推进系统。微推进装置的工作机理与常规推进装置存在很大不同,为更好地服务于微型飞行器,研究者们针对微推进装置中的不同组成部件展开了大量的研究工作。其中,作为微推进系统中的重要组成部件,微喷管内流动与工作性能研究是一个热点。微喷管的长度尺寸通常是微米级,其产生的推力一般为几微牛,由于目前的试验设备的精度不够,很难通过开展实验来研究微喷管的工作特性,研究微喷管的工作特性一般采用数值仿真方法。
气体的稀薄程度由努森数决定,努森数是气体分子的平均自由程(λ)与通道的特征尺度(d)的比值。根据努森数,流动可分为连续流(Kn≤0.001)、滑移流(0.001<Kn<0.1)、过渡流(0.1<Kn<10)和自由分子流(Kn≥10)。气体分子的平均自由程较大或者通道的特征尺寸较小时,流场中都会产生稀薄流动。
由于尺寸的缩小(至微米、纳米级),微喷管内流体流动具有跨流域的特点。在流动稀薄时,粒子间碰撞概率减小,能量交换不及时导致产生热力学非平衡现象,减小微喷管的推力,进而影响微推进系统的工作性能。同时,微喷管内流动具有马赫数大、雷诺数小(Re<1 000),喷管内流动基本是层流; 面积—体积比急剧增大,其流动特性、工作性能受喷管壁面条件影响增大等特点。
W.F. Louisos等[1-4]通过数值仿真研究了工作介质黏性、喷管形状、喷管加工深度、壁面热边界条件对微喷管内流动及其工作性能的影响。丁英涛等[5]结合实验与仿真,研究了微喷管中的质量壅塞现象。张根烜等[6]基于有无滑移的连续介质模型,对微喷管内流动进行仿真,同时研究了不同壁面条件对流动与工作性能的影响。Jinliang Xu等[7]采用带有速度滑移与温度跳跃边界条件的求解N-S方程方法进行数值仿真,主要研究的是喷管中的激波对流动的影响及不同入口压力、喉部直径时激波位置和形状的变化。F.La Torre等[8]针对微喷管中流体流动的跨流域特点,提出了将求解N-S方程和直接模拟蒙特卡洛(Direct Simulation Monte Carlo,DSMC)两种方法结合起来求解整个喷管内流场以及外流场。杨海威等[9]针对高温流体,考虑热力学非平衡现象引起的内能松弛问题,在DSMC中加入转动松弛过程研究入口压强和温度对微喷管内流动和工作性能的影响,但并没有研究转动松弛对微喷管工作的影响。王海韵等[10]研究了扩张半角、面积比以及刻蚀深度等几何结构参数对微喷管工作性能的影响。学者们大多研究的是微喷管边界条件对微喷管流动机理和工作性能的影响,对微喷管内的稀薄效应以及热力学非平衡现象分析较少。
本文仿真模型以NASA/GSFC设计的微推力喷管原型为基础,分别使用Fluent软件和OpenFOAM中dsmcFoam求解器进行仿真计算,对比求解带滑移边界的N-S方程和DSMC两种计算模型,研究稀薄效应对微喷管工作性能的影响以及通过在DSMC中配置不同气体分子转动松弛碰撞数Zrot的算例来研究微喷管中的热力学非平衡现象。
微喷管内流动属于跨流域问题,常常涉及到连续流、滑移流和过渡流等多种流态。常用的微喷管数值仿真方法有:基于连续性假设的N-S方程求解和带速度滑移、温度跳跃边界条件的N-S方程求解; 连续性假设失效时,可采用DSMC、分子动力学(Molecular Dynamics,MD)方法等求解微喷管内流动。
求解N-S方程即利用数值计算方法求解流体力学的基本控制方程,包括连续性方程、动量方程和能量方程等。在N-S方程求解滑移流过程中,常用的滑移边界条件有Maxwell滑移边界条件[11]、Gokcen条件[12]和Lockerby[13]条件。其中,由于Maxwell滑移边界条件的适用范围和精度相较于其他两种更高,具有重要的工程运用价值,其表达式为[14]
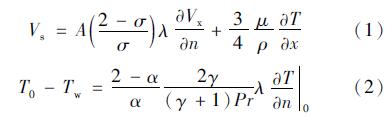
式中:μ为气体黏性系数; r为气体比热比; σ为动量调节系数; α为能量适应系数; λ为分子平均自由程; Vs为滑移速度; T0为壁面处流体温度; Tw为壁面温度。
曹文斌对上述方程的收敛性进行了研究,并给出了一种在任意网格下均能使计算收敛的边界条件处理方法,本文参考其边界条件处理方法,在Fluent中通过UDF形式实现滑移边界[15]。
DSMC仿真是基于统计学的数值仿真方法,用模拟粒子代替流场中的真实粒子(即用一个模拟粒子代替大量的真实气体分子),将模拟粒子的碰撞与运动过程解耦,通过模拟粒子运动的情况来表征真实流动; 在一个时间步长内,粒子分别完成运动和碰撞过程。dsmcFoam求解器是开源软件OpenFOAM中基于DSMC原理开发的,其中内能松弛通过Larsen-Borgnakke(L-B)内能松弛模型实现[16]。
由化学动力学知道,每一种气体分子自由度的激发和热力学平衡的建立都需要一定的时间,这种时间尺度即松弛时间。
在温度较高或者流动稀薄时,流动中热力学非平衡现象严重,分子松弛过程并不能用线性方程来描述,此时应用一般非线性方程
(dεi)/(dt)=f(ε,T,ρ,L)(3)
τi=τcZ(4)
式中:τc为气体分子平均碰撞时间; τi为所指定内自由度能量松弛过程的松弛时间; Z为气体分子自由度传能一次所需要的平均碰撞次数。由此可以定义气体分子碰撞之后松弛过程所指定内自由度的平均传能概率即碰撞松弛概率[17]
P=(τc)/(τi)=1/Z(5)
DSMC中首先是选取每个网格单元中可能发生碰撞的碰撞对同时确认其碰撞是否发生; 其次粒子间碰撞发生时,程序任意选取[0,1]间的随机数R,将碰撞松弛概率P与R进行比较,当P大于R时,即认为内能参与此次碰撞中的能量交换,由此实现热力学碰撞传能仿真,其过程如图 1所示。
因为文中计算工况中入口滞止温度为886 K,远小于气体分子(H2O,O2)的振动特征温度,因此只涉及到气体转动松弛,由式(5)可以定义气体分子碰撞后转动松弛过程的平均传能概率即碰撞转动松弛概率Prot=(τc)/(τrot)=1/(Zrot)>R,R∈[0,1](6)
当概率大于随机数R时,转动能参与能量交换。则可通过设定气体分子转动松弛所需要的松弛碰撞数Zrot来研究微喷管稀薄流动时的热力学非平衡现象。
为验证CFD和DSMC计算程序的正确性,分别采用Louisos和张根烜文章中的算例进行计算[6,18]。计算结果分别如图 2和图 3所示,对比分析可以看出,采用本文计算程序所得结果分别与文献[6]和文献[18]结果相近,Ma数图分布相近,说明本文采用计算程序可靠。
图2 Ma数分布的N-S方程计算方法验证
Fig.2 Verification of N-S equation simulation method for Mach number distribution
本文仿真模型以NASA/GSFC设计的微推力喷管原型为基础,扩张段为线性,喉部宽度为90 μm,出口截面宽度为560 μm,扩张半角α为10°~50°,扩张比保持不变[19]。图 4是微喷管几何模型示意图。
工作介质为过氧化氢(H2O2)分解产生的高温H2O和O2。边界条件为压力入口,入口压强1~250 kPa,入口气体(滞止)温度886 K; 微喷管工作环境为真空,即为0 Pa; 微喷管壁面在求解N-S方程时设置为Maxwell滑移壁面,而在DSMC中设置为漫反射壁面。采用ANSYS ICEM网格划分软件在直角坐标系下建立二维几何模型并进行网格划分,网格在喉部和壁面处加密,网格数为9万。为验证网格无关性,分别划分了疏密两种网格,对比流场与推力结果,网格疏密对结果影响很小,网格具有一定无关性。
常用的微喷管推力
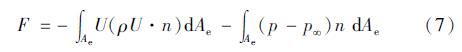
该公式适用于黏性效应不明显,即雷诺数足够大时的喷管推力计算。由于微喷管内流动雷诺数偏小,壁面条件对微喷管内流动影响显著,在计算推力时应考虑黏性效应对微喷管推力的影响。
J. M. Pearl等人在控制方程基础上,考虑黏性效应影响,推导出适用于微喷管推力[20]

比冲
Isp=F/(m·g)(9)
推力系数
Cf=F/(Atpin)(10)
式中:Ae为喷管出口截面面积; U为流体流动速度; ρ为密度; n为出口截面的外法线方向; p为流体在出口处的压强; p∞为环境压强; τ为切应力; m·是喷管中的质量流量; At为喷管喉部截面面积; pin为喷管入口压强。
本文仿真模型为二维,微喷管尺寸小,黏性效应严重,所以推力值均考虑黏性效应。
图5是由带滑移边界N-S方程计算结果处理得到的微喷管中心线上Kn数沿喷管轴向分布图。由图可以看出,随着入口压强减小,轴线上Kn数整体增加; 在入口压强等于50 kPa时,喷管内流动处于连续流到滑移流之间,微喷管出口附近流动出现Kn>0.1; 由流动状态的划分可得,微喷管内出现Kn数大于0.1的流动,连续性假设失效[21]。为研究稀薄效应对微喷管流动和工作性能的影响,取入口压强分别为1,5,10,50 kPa,分别用N-S方程+滑移边界和DSMC两种方法计算。
图6是不同入口压强时,微喷管出口截面处速度分布图。由图可以看出,随着入口压强减小,N-S方程计算结果与DSMC计算结果相差越来越大。与DSMC计算结果对比,无滑移N-S方程计算结果偏小,有滑移N-S方程计算结果处于两者之间。入口压强为50 kPa时,在微喷管出口核心流域,3种计算方法所得结果基本相同,差别主要出现在微喷管壁面附近。
结合图 5,在入口压强为50 kPa时,微喷管内处于连续流与滑移流之间,带滑移N-S方程基本能描述微喷管中的流动状态。入口压强为5,10 kPa时,N-S方程计算结果明显小于DSMC计算结果,特别是入口压强为1 kPa时,两者相差达到30%。这主要是因为求解N-S方程的计算过程是基于连续性假设,由此计算所得黏性大于由DSMC计算所得黏性,即基于连续性假设计算所得黏性大于实际稀薄流动中的黏性。黏性偏大,则流体流动过程受到的流动阻力就大,能量损失增加,故N-S方程计算得到的速度小于DSMC计算得到的速度。表 1是分别采用带滑移边界N-S方程与DSMC 方法计算得到的微喷管推力及比冲。由表中数据可以看出,相比于DSMC方法,N-S方程计算得到的微喷管推力、比冲均偏小; 且随着入口压强减小,偏差越来越大,在入口压强为1 kPa时,N-S方程的误差达到30%。这是因为入口压强减小,微喷管前后压降减小,微喷管壁面产生的流动阻力增大,流动变稀薄,导致由N-S方程估算的微喷管推力和比冲出现偏差。同时,结合图 6中微喷管出口截面处的速度分布分析,可以看出微喷管出口处速度误差与微喷管的推力性能误差近似相等,这说明,在微喷管推力计算中,速度冲量产生的推力基本可以确定微喷管推力的量级; 特别是在入口压强较大时,喷管出口处压强差产生的推力甚至可以忽略。
由以上分析可以看出,随着入口压强减小,微喷管中流动变稀薄。入口压强低于50 kPa时,微喷管中出现Kn数大于0.1的流动,连续性假设开始失效,求解N-S方程已不能描述这种稀薄程度的流动。稀薄效应明显时,壁面附近流体存在明显滑移速度,固体壁面对流体流动的阻碍作用减小,壁面造成的能量损失减小,气体工质中更多的内能转换成平动能,微喷管推力性能出现提升。
随着入口压强降低,微喷管中出现稀薄流动,分子间碰撞频率下降,造成粒子间能量交换不及时,进而对微喷管工作性能产生影响。选取入口压强为10,5,1 kPa,分别设置Zrot=1,5,∞,采用DSMC方法仿真研究微喷管中的热力学非平衡现象。由气体分子转动松弛所需要的松弛碰撞数Zrot的定义可知,Zrot表示的是系统要达到平衡状态所需要的每一个气体分子平均碰撞次数,即气体分子转动松弛所需要的松弛碰撞数。由式(6)可知:Zrot=1表示一种理想平衡状态,认为粒子的每一次碰撞中气体分子转动能均参与能量交换且交换后即达到平衡,称为内能平衡工况; Zrot=5则表示考虑微喷管中稀薄流动引起的转动松弛,气体分子转动能交换并不会发生在每一次粒子碰撞中,能量交换的不充分导致系统达到平衡需要一个过程,称为松弛工况; Zrot=∞即标志气体分子转动能不参与能量转换,称为内能冻结工况。
图7是不同入口压强下,微喷管出口截面处速度分布图。
图7 不同入口压强下微喷管出口截面处速度分布图
Fig.7 Velocity distribution at the exit of micro-nozzle under different inlet pressures
图8是不同入口压强下,微喷管出口截面处Ma数分布图。由图8可以看出,内能冻结工况的Ma数明显大于内能平衡工况和松弛工况。入口压强为10 kPa时,内能平衡工况和松弛工况Ma数分布相近; 随着入口压强减小,Ma数受转动松弛的影响增大,在入口压强为1 kPa时,松弛工况与内能平衡工况差别达到3%左右。结合速度分布图分析,松弛工况的Ma数大于内能平衡工况,这与速度分布图中的趋势相反。结合Ma数的计算公式可得

式中:v为气体流动速度; k为气体比热比; R为气体常数; Ttr为气体分子的平动温度。
Ma数受平动温度影响更大,考虑转动松弛使系统平动温度和流场速度均减小,但平动温度减小量大于流场速度减小量,因此反而使得Ma数增大。对比分析可以得出,转动松弛对微喷管内速度场影响相对较小,对温度场影响较大。微喷管推力计算方法与2.1.2节相同。表 2是不同入口压强、不同Zrot下计算所得微喷管的推力与推力系数。
表2 不同入口压强和Zrot时的微喷管推力性能
Tab.2 Thrust performance of micro-nozzle under different inlet pressure and Zrot
由表2中数据可以看出,松弛工况计算得到的推力比内能平衡工况计算所得推力小,随着入口压强减小,转动松弛引起推力的相对偏差增大,入口压强为1 kPa时达到1%。结合微喷管出口截面处速度分布图,转动松弛对微喷管出口截面处速度的影响在1%~2%之间。微喷管推力误差小于出口截面处的速度误差,这是因为入口压强太低,前后压强差偏小,微喷管中黏性作用明显,由速度冲量产生的推力占比减小,由出口处压强差产生的推力占比增加,此时微喷管推力不再与出口速度成正比,出口处压强差对微喷管推力的影响增加。
通过求解带滑移边界的N-S方程与DSMC方法,研究了微喷管内稀薄流动以及发生稀薄流动时的热力学非平衡现象,得出结论:
1)微喷管中出现Kn数大于0.1的过渡流时,连续性假设失效; 考虑稀薄效应在一定程度上提升了微喷管的推力性能。
2)微喷管中发生稀薄流动时,热力学非平衡现象并不会立即对微喷管的流动及工作性能产生影响,而是在稀薄流动达到一定程度后才会产生影响; 受热力学非平衡现象影响,微喷管推力性能变差; 微喷管内温度场受热力学非平衡现象的影响大于速度场。
3)微喷管内流动状态复杂,在进行仿真研究时应根据微喷管内的流动状态选择相应的仿真方法:连续性流动时选择N-S方程; 连续性假设失效时选择DSMC方法; 流动达到一定稀薄程度时,还需要考虑热力学非平衡效应。