基金项目:国家自然科学基金(11602186)
作者简介:尹继辉(1995—),男,硕士,研究领域为火箭发动机热过程。
通信作者:郑东(1987-),男,博士,研究领域为碳氢燃料燃烧化学反应机理。
1西南交通大学 机械工程学院,四川 成都 610031; 2西安航天动力研究所 液体火箭发动机技术重点实验室,陕西 西安 710100
1School of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China; 2Science and Technology on Liquid Rocket Engine Laboratory, Xi'an Aerospace Propulsion Institute, Xi'an 710100, China
monomethylhydrazine; nitrogen tetroxide; reaction mechanism; simplified mechanism; ignition delay time; flame temperature
采用反应流分析结合灵敏度分析的简化方法,对前期研究发展的MMH/NTO详细燃烧化学反应机理进行了简化,获得包含25个组分和43个基元反MMH/NTO简化反应动力学模型。并从着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度两方面,通过对比理论结果、详细机理和简化机理预测结果,在较宽范围参数内对简化机理进行了验证。验证结果表明简化机理和详细机理预测的MMH/NTO体系的着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度具有非常高的一致性,说明了简化反应机理的合理性。进而分析了初始温度、燃烧室压力、以及氧燃比对MMH/NTO体系的着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度的影响规律,MMH/NTO体系的着火特性对初温和燃烧室压力较为敏感,燃烧火焰温度则对氧燃比和燃烧室压力较为敏感。为后续发动机燃烧的CFD数值计算提供了准确的反应动力学模型。
In this paper, reacting flow analysis combined with sensitivity analysis was used to simplify the detailed chemical mechanism of MMH/NTO hypergolic propellants developed in our previous research. Andthereduced kinetic model consistingof 25 species and 43 elementary reactions was obtained. From ignition delay time and combustion flame temperature, the reducedmodel has been validated againstthe theoretical results and detailed model at widerconditions. The validation shows that the ignition delay timesandcombustion flame temperatures predicted by the reduced model arehighly consistent with thatofthe detailed model.Furthermore, the influence of initial temperature, chamber pressure and oxygen/fuel mass ratio on the ignition delay time and combustion flame temperature was analyzed.The results show that the ignition characteristics of MMH/NTO bipropellant systems are more sensitive to initial temperature and chamber pressure, while the combustion characteristics are more sensitive to O/F and chamber pressure. The present research provides areducedand accurate kinetic model for multi-dimensional CFD(Computational Fluid Dynamics)combustion simulation in engine combustor.
双组元自燃推进剂具有常温常压下正常贮存、无需任何点火源即可自燃着火燃烧的优点,被广泛应用于运载火箭发动机及空间姿轨控发动机[1]。鉴于甲基肼(MMH)和四氧化二氮(NTO)由于具有优良的燃烧化学特性,被广泛用作双组元液体火箭发动机推进剂[2-3]。对于MMH/NTO燃烧化学反应动力学模型研究的重要性体现在两方面:一是化学反应机理不仅有助于深入理解其燃烧过程、揭示燃烧机理和规律,对理解火箭发动机内部工作过程,特别是燃烧室内的燃烧过程具有重要意义,也为实现定量、准确的发动机燃烧数值模拟提供必要的燃烧模型[4-5]。二是MMH/NTO毒性大、腐蚀性强、高致癌性,且具有很高的反应活性,即使在低温、高稀释条件下仍能发生反应,很难通过实验研究MMH/NTO的基础燃烧特性[6],也尚未见文献报道。采用化学反应机理预测其基础燃烧特性就显得尤为重要。
针对MMH/NTO化学反应动力学模型,目前仅有少量的公开发表文献进行报道。其中,Catoire等通过分析MMH/NTO体系的反应过程[7],整合其前期研究[8-9]与相关文献的反应路径,并基于量化计算补充相关组分的热力学参数,提出了82组分、403个基元反应的详细反应动力学模型,但却未公开其模型的更多细节。巴延涛等依据MMH/NTO体系的冷反应、热分解反应、自燃着火反应、以及高温反应四个阶段,甄选每个阶段的主要反应[10],从而发展了23组分、20个反应的骨架反应机理。但由于部分反应路径缺失,导致燃烧无法达到理论平衡状态。王大锐等采用主成分联合多代通量对某机理(未公开)进行简化[11],从而获得33组分、111个基元反应的简化机理,但其文中也缺少对简化机理的描述。
此外,与MMH/NTO反应机理相关的研究也有一些文献报道。Sun等在激波管中研究了MMH热分解过程,并发展了其热解反应机理[12-13]。Liu等采用实验与量化计算方法,研究了MMH/NO2、N2O4初期反应过程,并提出了着火前的气相反应与发烟反应机理[14]。Kanno等基于过渡态与RRKM理论,研究了MMH通过NO2的脱氢反应及其逆反应,并获得其反应动力学参数[15-16]。这些相关研究为发展MMH/NTO化学机理奠定了基础。
综上所述,目前针对MMH/NTO详细反应机理研究极少,反应机理的细节并未公开,且详细机理过于复杂,并不适用于火箭发动机的多维燃烧CFD数值模拟。而总包反应机理忽略了中间反应,数值计算结果与实验测量结果出入较大,通常需要修正反应参数才能获得合理的计算结果,这就极大限制了总包反应机理的适用范围。因此,对于适度规模的简化反应动力学模型研究具有重要的工程应用价值。本文将以前期研究发展的MMH/NTO详细反应机理为基础,采用反应流分析结合灵敏度分析简化方法,获得规模适中的MMH/NTO简化反应动力学模型。并通过与详细机理的对比,验证简化反应机理的准确性。
反应流分析是常用的机理简化方法之一[17],依据组分所涉及基元反应的相对产率系数,确定组分的主要反应路径(相对产率系数大于临界阈值),找出节点组分和重要基元反应,建立从初始反应物到最终产物的路径图。相对产率系数
 (1)
(1)
式中:vki和qi分别为第i基元反应的反应速率、化学计量系数; I为所有涉及到k组分的基元反应数目的总和。
反应流分析可以清晰展现从反应物到产物的整个主要反应过程,能有效地进行机理简化。但该方法可能会忽略某些产率系数较小,但却具有较高的组分或温度灵敏度系数的反应,这些反应虽然不体现在主要反应路径中,但却能对组分或系统温度有很大影响。因此,进行组分灵敏度分析和温度灵敏度分析[18-19],补充灵敏度系数较大的基元反应(灵敏度系数大于临界阈值),以提高机理简化的精度。组分所涉及基元反应的敏感性系数。
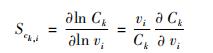 (2)
(2)
反应对系统温度的敏感性系数。
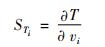 (3)
(3)
式中:Ck为k组分浓度; vi为i基元反应的反应速率; T为反应系统温度。
机理简化主程序的核心结构分为反应流分析程序流程、组分灵敏度分析程序流程和温度灵敏度分析程序流程。如图1所示为反应流分析程序流程,首先,以燃料组分为循环起始组分,进入反应循环计算每一个基元反应对该组分的产率,当产率大于阈值时,该基元反应逻辑变量设为真(即该反应重要,需要保留),该基元反应中的组分逻辑变量设为真(即该组分重要,需要保留)。
阈值越低,简化精度越高,但简化后机理规模较大; 阈值越高,机理简化程度越大,但简化精度降低,因此本文中产率、组分灵敏度和温度灵敏度阈值均设置为0.1。完成初始组分的反应循环后,得到初始反应物的主要反应路径和生成的组分(即节点组分)。其次,对于每个节点组分,再进行与上述初始组分相同的反应循环,以此类推就可以获得整个反应路径的重要组分和重要基元反应。最后,取其所有节点组分和重要基元反应,即构成简化机理。
图2为组分灵敏度分析程序流程,与反应路径分析程序流程类似,但有不同。组分循环从第一个开始,判断该组分是否为节点组分,若不是则进行下一个组分,若是则该组分进进入反应循环计算,计算每一个基元反应对该组分的灵敏度,获得灵敏度系数大于阈值的基元反应,以及基元反应中的组分,这些反应和组分对反应路径分析所获得简化机理,进行有效的补充,提高简化机理的精度。
温度灵敏度分析是确保对反应系统温度有一定影响的基元反应合理保留,以提高简化机理在预测着火、燃烧特性方面的准确性。图3为温度灵敏度分析程序流程,温度灵敏度分析程序流程是从第一个反应开始的反应循环,判断该反应的温度灵敏度系数是否大于阈值,再对每个反应都进行判断,获得温度灵敏度系数大于阈值的基元反应,以及基元反应中的组分,这些反应和组分对简化机理进行有效的补充,进一步提高简化机理的精度。
前期研究中通过整合MMH热解反应机理、NTO热解反应机理、MMH/NTO及其中间组分反应机理、以及小碳氢组分反应机理,提出了包含72个组分、406个基元反应的MMH/NTO燃烧化学反应动力学模型。并通过着火延迟时间、温升曲线、火焰温度的理论值和现有反应机理的预测结果,验证详细反应机理的准确性[20]。本文采用上述开发的机理简化程序,对该详细反应机理进行简化,获得包含25个组分、43个基元反应简化反应动力学模型,该简化模型的准确性将在下一节中进行充分的验证。
鉴于目前尚未有公开发表的MMH/NTO体系基础着火燃烧特性参数实验数据。因此,本文用CHEMKIN[21]在零维、均质、绝热、定容/定压模型中计算MMH/NTO着火延迟时间与燃烧火焰温度(即平衡温度)。通过对比理论结果、详细机理预测结果、以及本文简化机理预测结果,从着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度两方面,验证简化机理的合理性。
采用定容燃烧模型计算了初始温度298 K和286 K、混合气组成MMH+2.5NTO(1.0275N2O4+1.4725NO2)、MMH/NTO着火延迟时间随压力的变化,并与Seamans等[22]依据热爆炸理论得到的着火延迟时间进行了对比(图4所示)。简化机理预测的着火延迟时间与详细机理预测值基本重合,很好地反映了MMH/NTO的着火延迟时间的压力依赖特性,说明了简化的合理性。初温298K时简化机理在整个压力范围所预测的着火延迟时间与Seamans等得出的结果高度吻合,而初温286 K时简化机理预测值虽然略低于理论数据(这是由于详细机理预测值略低于理论值,这是由于低温下动力学参数不准确),但其偏差仍在可接受的范围以内。
进一步在更宽的初始温度270~900 K、燃烧室压力0.1~10 MPa、氧燃比(氧化剂与燃料质量比)0.4~3范围内,通过对比简化机理和详细机理计算的MMH/NTO着火延迟时间,更全面充分验证简化机理的合理性。液体火箭发动机燃烧是定压燃烧过程,因此CHEMKIN计算采用采用定压求解。由图5可见,在更宽的温度、室压、氧燃比范围内简化机理预测值与详细机理预测值几乎完全重合,充分说简化机理在预测着火延迟时间的准确性。此外,初温/压力对MMH/NTO体系着火延迟时间均有较大影响,随初温/压力增大着火延迟时间迅速减小。氧燃比对MMH/NTO体系着火延迟时间有一定影响,随氧燃比增大(即由富燃向贫燃转变)其着火延迟时间逐渐增大,这是因为化学反应速率与速率常数和反应物浓度成正比,根据阿伦尼乌斯方程k=Ae-Ea/RT,温度T增大,速率常数k增大,反应加快; 初始压力增加,反应物的浓度增大,反应加快。此外温度、压力、氧燃比对反应路径也有一定影响,从而影响其反应速率。这一规律与传统碳氢燃料着火特性相似。
在上述相同的更宽初始温度、燃烧室压力、氧燃比范围内,验证简化机理在计算的MMH/NTO燃烧火焰温度方面的准确性。图6给出了简化机理和详细机理预测的MMH/NTO体系定压燃烧火焰温度随初始温度、燃烧室压力以及氧燃比的变化曲线。
由图可以看出简化机理预测的燃烧火焰温度与详细机理保持一致,其平均偏差不超过1%,说明简化机理在预测宽参数范围的燃烧火焰温度也是准确的。此外,在氧燃比为1.4、燃烧室压力为2.0 MPa,氧燃比为1.65、燃烧室压力为2.0 MPa与氧燃比为1.65、燃烧室压力为5.0 MPa三种情况下,可见MMH/NTO体系燃烧火焰温度随初温增大呈现小幅增加,说明初始温度对其火焰温度的影响较小。初温为298K时,在氧燃比为1.4和1.65两种情况下的结果可以看出,燃烧室压力对MMH/NTO体系火焰温度有一定影响,总体上都呈现先快后慢的增加趋势。对比初温为298K,燃烧室压力分别为1、2、5 MPa三种情况可以得知,氧燃比对MMH/NTO体系火焰温度影响都很大,呈现随氧燃比增大先快速增大、后缓慢减小的趋势。当氧燃比为2.0附近燃烧火焰温度达到峰值。
本文以前期研究发展的MMH/NTO详细燃烧化学反应机理为基础,采用反应流分析结合组分、温度灵敏度分析简化方法,提出了包含25个组分和43个基元反应的MMH/NTO简化反应动力学模型,为后续CFD数值模拟提供了规模适中的燃烧反应机理。从着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度两方面,通过对比理论结果、详细机理预测结果、以及本文简化机理预测结果,对简化机理进行宽范围参数(初温270~900 K、燃烧室压力0.1~10 MPa、氧燃比0.4~3)的验证。验证结果表明简化机理和详细机理预测的MMH/NTO体系的着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度具有非常高的一致性,充分说明了简化反应机理的合理性。
分析了初始温度、燃烧室压力、以及氧燃比对MMH/NTO体系的着火延迟时间和燃烧火焰温度的影响规律,MMH/NTO体系的着火特性对初温和燃烧室压力较为敏感,燃烧火焰温度则对氧燃比和燃烧室压力较为敏感。