基金项目:国家自然科学基金青年基金(52005385)
作者简介:张凭(1993—),男,博士,工程师,研究领域为液体火箭发动机高温组件疲劳寿命。
1.西安航天动力研究所 航天液体动力全国重点实验室,陕西 西安 710100; 2.航天推进技术研究院,陕西 西安 710100
1. National Key Laboratory of Aerospace Liquid Propulsion, Xi'an Aerospace Propulsion Institute, Xi'an 710100, China; 2.Academy of Aerospace Propulsion Technology, Xi'an 710100, China
reusability; liquid rocket engine; regeneratively-cooled thrust chamber; thermal-mechanical failure; fatigue life prediction
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9374.2024.01.002
液体火箭发动机性能高、适应性强,是运载火箭、航天飞机等航天运载器的主要动力装置[1],而重复使用运载器是未来航天领域的重要发展方向。再生冷却推力室作为重复使用液体火箭发动机的关键部件,工作环境和载荷较为严苛,是影响发动机使用寿命的关键组件。
现代高性能液体火箭发动机推力室室压可超20 MPa,燃气温度可达3 500~4 000 K,推力室喉部热流密度最大可达160 MW/m2[2-3]。为保证推力室内壁结构工作在合适的温度下满足承载能力要求,推力室通常采用再生冷却方案(见图1)。推力室内壁通常采用导热系数较高的铜合金,而铜合金抗腐蚀及高温承载能力较低,因此一般采用涂/镀层工艺降低内壁基体结构工作温度、提高抗腐蚀及抗冲刷性能。长时间工作时,涂/镀层在热-力-化学作用下开裂并剥落,而内壁在两侧温度梯度和压差作用下产生显著塑性变形; 对于重复使用发动机,在启动、关机、变推力、高空二次启动和反推回收等工况下,推力室内壁将反复承受热冲击、短时超压和水击等恶劣载荷,结构内低周疲劳、蠕变、热棘轮和化学等耦合损伤不断累积,最终发生图1所示的热-机械疲劳失效—“狗室”(dog house)失效,严重影响组件安全及性能。推力室内壁失效作为重复使用发动机研制的瓶颈问题一直备受关注,美、德、俄、日等国从20世纪60年代至今开展了大量试验和数值研究工作,旨在明晰其失效机理并发展疲劳寿命评估方法,识别关键敏感因素以优化结构设计及系统参数。
我国当前正开展多种型号的重复使用液体火箭发动机研制/预研工作,为支撑研制过程中推力室的设计与验证,迫切需要开展推力室再生冷却结构的热-机械疲劳分析方法研究。因此,本文对内壁热-机械疲劳分析方法发展历程进行梳理,重点分析材料本构关系、热-力响应计算和疲劳寿命分析模型与方法,最后基于研究进展与工程需求提出进一步研究的方向和建议。
从20世纪60年代至90年代中期,以航天飞机主发动机(Space Shuttle Main Engine,SSME)为应用背景,NASA Lewis Research Center(LeRC)的学者率先针对再生冷却推力室内壁的热变形及疲劳问题开展研究。2000年后,相关研究与NASA的航天飞机计划一同暂停,而德国由于承担了欧洲运载火箭研发任务而成为推力室内壁失效研究的中心。回顾研究历程(见表 1),推力室内壁疲劳寿命分析方法与材料本构关系、数值求解方法和疲劳寿命模型交替发展,并在计算机技术、有限元软件和试验技术的推进下逐步由早期的等温低周疲劳分析发展为目前最新的基于连续损伤模型的热-机械疲劳分析。
表1 推力室内壁疲劳寿命分析方法发展历程
Tab.1 Development of fatigue life analyzing methods applied to thrust chamber walls
1967年,Boelkow GmbH和Rocketdyne公司研究发现OFHC铜合金推力室的疲劳裂纹[4-5],由此引发热-力疲劳问题研究。随后LeRC通过13个燃烧室循环热试[6]和寿命预估工作[7]发现内壁并非典型的疲劳失效而是棘轮加速的蠕变断裂。Quentmeyer开展了22台柱塞式喷管的热试验,发现循环次数增加时,推力室内壁厚度不断变小且向燃气侧突出直至断裂[8]。该工作首次将推力室内壁故障定义为沿用至今的“狗室”失效。Hannum等测量不同材料推力室循环热试验后变形状态[见图2(a)],有力支持了“狗室”失效理论[见图2(b)],同时指出结构失效诱因是随循环线性累积的变形,即棘轮变形[9-10]。
限于热结构疲劳的力学理论、数据积累和硬件条件,该阶段热-结构数值分析和疲劳寿命预测方法采用了较多假设和简化,采用循环稳定状态下的材料应力-应变关系、等温疲劳试验的应变幅-寿命关系和线性损伤累积法评估结构的疲劳寿命[11-12]。
LeRC的主管Quentmeyer[8]认为,即便采用等温疲劳试验数据[13-18],预测寿命和试验结果的一致性仍不理想; 而随后开展的试验表明延性断裂才是结构寿命的瓶颈[19],失效分析必须考虑材料的拉伸不稳定性。该阶段产生了大量著名的材料统一黏塑性本构关系,但限于当时的硬件条件,大规模逐循环的弹塑性求解无法实现,因此衍生出一系列简化的解析和半解析方法,如Porowski简化模型[19-20]和Dai-Ray夹芯梁简化模型[21]等。随着计算机技术和商业有限元软件的发展,统一黏塑性本构因其出色表现而被用来获得更真实的结构热-力学响应。虽仍采用应变疲劳理论,但该阶段工作可考虑变温状态下的材料性能,并基于线性损伤理论逐循环叠加损伤[22]。该方法已基本满足工程需求,同时标志着NASA主导阶段的结束。
2000年左右,德国转变为推力室疲劳寿命前沿研究的中心。戴姆勒奔驰宇航中心(Dasa)和德国宇航中心(DLR)在1996年合作开展低温火箭推进计划(TEKAN)以支持下一代的欧盟火箭,开展了一系列基础理论、数值分析和试验工作,对重复使用高性能推力室进行评估改进[23]。DLR开创性地利用激光加热的方法建立了推力室结构的“热-机械疲劳”(Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue, TMF)平板试验系统[24-27](见图3),探索结构在极端热冲击和热梯度下的热-机械疲劳和蠕变特性,陆续验证了流场、温度场、结构响应和疲劳寿命分析结果。而Fassin等设计了可更换疲劳试样的GOx/GCH4矩形推力室模块化试验装置,研究热、力及化学交互作用并验证数值模型的合理性[28]。在充足的试验验证和数据积累下,德国科研人员开展了基于延性耗竭和连续损伤理论的内壁失效研究。
基于NASA发展的应变疲劳黏塑性分析方法,DLR的团队以Ariane 5火箭的Vulcain发动机推力室为对象,系统分析了有限元模型类型、载荷施加速率、本构关系、瞬态热分析等对推力室热-结构变形和疲劳寿命的影响[29-31]。在对比试验和仿真结果后,Riccius引入了基于延性耗竭的准静态疲劳概念[31],基于循环载荷下的累积残余拉应变计算准静态损伤,解决了预测失效点与试验不一致的难题。
准静态疲劳分析虽可定位内壁失效点,但仍无法充分描述“狗室”失效行为。Tini等[32-33]根据连续损伤力学理论建立了耦合损伤的黏塑性本构关系,并进一步引入材料蠕变损伤、老化效应[34-35]、裂纹闭合影响[36]等因素,成功描述“狗室”变形及结构疲劳寿命。作为该领域最前沿的方法,CDM虽然实现复杂但对推力室内壁失效行为描述效果最理想。
推力室的热疲劳分析实质上是建立材料热/力学特性模型,根据既定边界和载荷采用数值模型分析热-力学响应,并采用热-机械疲劳寿命理论评估损伤发展的工作。以往研究各有侧重,发展了众多新理论、新方法,现进行简要梳理。
推力室内壁工作于变温环境中,承受循环热-机械载荷且存在蠕变、冲刷和化学侵蚀等长时损伤影响。内壁材料一般选用铜合金,该类材料对温度和加载率敏感且表现出不同程度的循环硬化/软化特性。为了精确描述材料的力学响应,研究人员在不同工程需求和时代背景下采用了以下3类本构关系,各自代表性工作见表 2。
表2 推力室力学响应分析采用本构关系
Tab.2 Constitutive relations adopted in the analysis of thrust chamber wall's mechanical responses
早期研究及工程计算较多采用经典弹塑性本构,如Miller[11-12]采用RETSCP程序[37]对LeRC热试失效的氢氧发动机进行三维弹塑性分析。该类本构采用理想弹塑性假设或基于试验数据拟合等向/随动强化特性,无法考虑时间相关行为。由于不包含蠕变行为,需要配合Norton等蠕变本构使用。
同时由于推力室内壁铜合金显著的率相关硬化/软化特性,该类本构误差较大。Armstrong等研究了不同材料及组合形式下的推力室身部响应后指出,材料数据的缺乏导致简化的本构关系无法描述强化及率相关特性,而结构应变率(最大0.2/s)与材料试验(0.01/s)存在数量级差异,且所选材料具有显著的率敏感特性[38]。Riccius等对比了数值仿真和TMF试验结果后指出,经典弹塑性模型分析结果与试验相差10倍以上[45]。随着商业有限元软件和计算机的发展,该类本构逐渐被统一黏塑性本构所代替,但当材料试验数据缺乏或材料无明显循环演化行为时,其仍是力学响应计算的普遍选择。
统一黏塑性本构将总应变率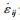 分解为弹性应变率
分解为弹性应变率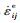 、非弹性应变率
、非弹性应变率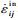 和热应变率
和热应变率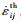 ,即
,即
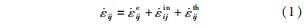
非弹性应变率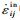 中包含塑性应变、蠕变及松弛效应,其变化规律由流动准则描述,其中包含一定数量的与时间相关的内变量,刻画材料的硬化、软化和恢复效应; 内变量的变化规律由演化准则描述。根据是否含有屈服面可分为第一类(含有屈服面)和第二类(不含屈服面)统一黏塑性本构。
中包含塑性应变、蠕变及松弛效应,其变化规律由流动准则描述,其中包含一定数量的与时间相关的内变量,刻画材料的硬化、软化和恢复效应; 内变量的变化规律由演化准则描述。根据是否含有屈服面可分为第一类(含有屈服面)和第二类(不含屈服面)统一黏塑性本构。
第一类本构以Chaboche本构[64, 90]为代表,因其在商业有限元软件中的成功置入而被广泛采用。如Asraff采用三项叠加的Chaboche随动强化准则和Voce等向强化准则得到了循环加载下的内壁危险点应力-应变响应[65],开展铜合金试验并对比了不同等向强化和随动强化对铜合金力学响应描述的差异,发现Chaboche本构关系可更好地适应推力室仿真[91]; 羽中豪等采用Chaboche本构分析了不同室压、推力和混合比设计方案的棘轮应变[66]。
第二类本构以Robinson[73]和Freed本构[92]为代表。两者均在NASA的研究计划推动下产生[93],广泛用于航天结构,能定性地再现长时载荷下冷却通道底部不断凸出与变薄的现象,具有精确预测结构寿命的能力。如Robinson等采用Robinson本构计算SSME推力室喉部的棘轮-屈曲失效特性,发现交变载荷下的动态和热恢复效应对蠕变屈曲影响显著,而采用不含恢复效应的本构关系将导致非保守的蠕变寿命预测[70]。文献[71-72,74]在通用有限元软件Marc中实现了Freed本构[92]和Robinson本构[73],分析了铣槽式和管束式推力室的内壁变形,发现内壁失效与非均匀的压力梯度和运行时间高度相关。杨进慧等在Marc软件中仿真NARloy-Z材料的高温力学特性和内壁失效过程,与NASA报告的对比验证了Robinson本构可以较好地表征高温下材料特性和“狗室”失效模式[75]。
统一黏塑性本构对材料的时间/热恢复行为描述更简便,对材料硬化和软化行为描述更精确,在当前阶段应用最广泛; 但其参数较多,需要大量试验数据来拟合。
损伤本构是以黏塑性本构和Lemaitre等损伤模型为基础衍生的各类描述材料性能衰退的本构关系。根据Lemaitre损伤理论,连续损伤变量的演化过程可表示为[94]
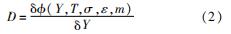
式中:φ(Y,T,σ,ε,m)是与应力状态、弹性/塑性/棘轮/蠕变应变状态、温度、材料属性等相关的函数; Y为应变能释放率。
根据Lemaitre应变等价假设将本构关系中的应力项σ替换为等效应力σ^-,可建立耦合损伤本构关系,即
σ^-=σ/(1-D) (3)
损伤本构目前多为德国研究人员采用,可描述老化、损伤、蠕变、侵蚀等导致的材料性能衰退。如德国Astrium GmbH公司的Schwarz等基于损伤本构仿真了推力室内壁失效过程,考虑了高温下材料的应力松弛、应变率相关特性、各向同性和随动强化特性,通过修改硬化参数反映老化效应并通过分解拉/压应力分量引入微缺陷闭合效应[86]。Kowollik基于A-F随动强化、Voce等向强化、Perzyna率相关特性和Lemaitre延性损伤特性定量描述“狗室”变形程度[63]。该类本构实现难度大,参数定义多样且识别难度较高,但更适用于复杂热-力-化学环境下的渐进损伤分析,是目前推力室内壁分析中最具潜力的材料本构关系。
内壁热-力响应计算涉及热对流、热传导、热变形、机械变形等物理过程,可采用解析方法和有限元方法求解控制方程,最终获得结构应力-应变历程。解析方法采用简化力学模型,可快速计算内壁变形量,适用于方案优化和在线动态损伤评估; 有限元法精度更高,适用于精细化响应和寿命分析。而半解析方法通过特定时间点的有限元节点位移插值获得全循环形变结果,目前较少使用。表 3中列举了部分较典型的响应计算研究工作。
半解析方法由Armstrong[41]提出,采用预测-修正的解析算法将10个热试循环数值分析的薄化量曲线外插到200循环以预测结构失效点,并在100、200循环进行弹塑性分析修正插值过程[42]。后续研究中考虑了材料的软化和硬化特性,通过插值有限元节点位移获得外插的结构变形量。
为了建立高效简便的寿命设计流程,文献[19-20]建立了冷却槽简化矩形梁模型,以解析法计算应变并与Marc软件的有限元计算结果对比,精确性在可接受范围; 随后Robinson等采用理想Shanley夹心柱(梁)模型解析计算SSME推力室喉部的棘轮-屈曲失效特性[70]。与此同时,由于SSME的大规模使用和维护,LeRC开展了发动机减损控制研究,旨在兼顾发动机性能和负载[97]。为在使用中(循环内部)评估损伤并动态调整控制策略,Dai等[21]采用夹心梁模型[70]及Freed本构[92]实时解析计算内壁薄化量。
有限元分析目前被广泛应用于内壁失效和寿命分析,文献[56-57]开发了热-力耦合有限元程序,系统分析了推力室中冷却剂流动、壁面换热过程、结构传热和热变形问题,讨论了建模方法差异、内壁失效机理和影响因素。基于等向强化本构关系的研究表明,采用瞬态热分析计算的结构寿命降低40%以上,而推力室中温度和压力高频振荡造成的高周疲劳损伤可忽略[31]。后续引入Peirce率相关模型的研究表明,率相关本构和瞬态热分析对结构响应和疲劳寿命预测至关重要[29]。而对平面应变、广义平面应变[30]和三维模型[96]的对比发现,平面应变模型预测的循环寿命最低。Armstrong的三维热-结构分析指出二维模型即可满足热响应分析精度要求,但热-力应变分析需用三维模型[40]。
目前热-力响应有限元分析采用单、双向耦合两种方式,单向因耦合计算简便而被广泛采用,如印度液体火箭推进系统中心(LPSC)的Asraff等采用单向耦合分析氢氧和液氧/煤油发动机推力室响应和疲劳寿命[58-59]; 张亮等采用二维单向耦合简化模型分析了内壁的热疲劳寿命[49]。双向耦合理论上可反映结构形变对热力学过程的影响,如文献[53-55]采用流固耦合计算沿轴向三维再生冷却槽道的热机构变形[见图4(a)]和低周疲劳寿命,分析了冷却流道和冷却剂参数对疲劳寿命的影响,但其计算代价高且目前研究未明确表明其对精度的提升效果。
热过程分析普遍采用二维稳态计算以形成稳态温度载荷曲线,早期虽有瞬态分析,但实际是线性插值处理的稳态载荷[11-12],如Armstrong等[38]基于发动机冷/热态工况载荷曲线[见图5(a)]进行的流-热分析和平面应变模型[见图5(b)]求解,并不能反映启动、关机过程的瞬态热冲击载荷影响。目前研究表明瞬态载荷对内壁失效影响显著,如孙冰等的三维瞬态热分析研究表明内壁温度约0.10 s达到稳态,明显快于外壁; 瞬态分析得到的最大残余应变比稳态分析高15.7%[见图4(b)],损伤水平更高[61]。
随着燃烧室状态、室壁沉积物和涂层等因素的变化,流动和温度场的经验计算结果将偏离试验真实值[3],而采用试验测量数据与瞬态分析耦合的策略,可在验证CFD结果的同时修正流动和温度场与经验计算的差异。如文献[67-69]基于Song等[98]的湍流燃烧CFD方法和结果,在FLUENT中进行流动-传热分析获得温度和压力载荷三维分布[67],后期采用试验测量结果作为输入数据[68],利用非线性有限元分析结构应力-应变响应[见图6(a)]并基于Riccius等[30]的方法评估结构的准静态损伤。该方法对DLR的TMF平板试验仿真结果与试验观察一致性较好[见图6(b)]。
随着内壁损伤机理认知的深入,疲劳寿命分析模型和方法也不断衍生,可大致分为传统低周-蠕变寿命模型、Porowski塑性失稳模型、Dai-Ray内壁薄化模型、Riccius准静态疲劳模型和连续损伤模型。目前传统低周-蠕变寿命模型和准静态疲劳模型被广泛采用,二者区别为是否考虑延性耗竭损伤,而基于连续损伤模型的研究是当前热点。表 4中给出上述模型的基本形式和代表研究供参考。
传统低周-蠕变模型以局部应力应变法和Miner线性损伤累积理论为基础,采用Manson-Coffin公式计算失效点在特定循环应变幅下的疲劳寿命和损伤,基于蠕变持久试验数据计算蠕变损伤,根据载荷分频计算损伤和寿命。工程适应性强,试验数据需求相对较小,但预测寿命分散性大。Miller基于材料等温疲劳数据和修正的通用斜率公式预测低周疲劳寿命:预测寿命为80循环,而实际试验裂纹萌生寿命为39循环[11-12]。Riccius等模拟TMF结构变形并采用Manson-Coffin公式计算疲劳寿命,预测结果比试验值低32%,且预测失效点和结构变形状态与试验不一致[62]。但由于各损伤组分独立,该模型便于剖析各损伤影响及变化。Armstrong等采用应变-寿命曲线预测结构疲劳寿命,参数研究发现降低热膨胀率、提高热传导率可以降低非弹性变形[38-39]。Asraff等给出了低周、蠕变、棘轮损伤对内壁失效的影响占比[91]。程诚等分析了结构内疲劳损伤随工作循环的变化趋势和分布,发现随着工作循环的上升,残余应变线性累积,疲劳损伤非线性增长[53-55]。
文献[19-20]基于冷却槽简化矩形梁解析模型计算内壁挠度,建立寿命分析模型:忽略随动强化影响并假设循环中内壁薄化率不变,提出基于临界厚度的塑性失稳准则并计算塑性失稳寿命; 同时基于疲劳寿命试验数据分析低周疲劳寿命,以停止薄化厚度作为判定结构塑性失稳和低周失效的临界点。考虑到SSME的冷却剂压力较高且运转时间长,Dadlani等进一步基于Norton律引入蠕变效应,根据Robinson时间分数损伤和Kachanov连续损伤理论计算蠕变损伤,提出考虑蠕变断裂的Porowski模型[43]。北京航空航天大学的杨进慧等[47]采用蠕变修正的Porowski寿命模型分析SSME的NARloy-Z内壁在热载荷下的使用寿命,研究了随动强化对结构分析的影响[60],分析了“狗室”失效中内壁厚度和蠕变应变随加载次数的变化规律。Porowski模型简单易用,其停止薄化厚度的提出与棘轮安定性的概念相似。虽然基于解析方法建立,但其寿命分析准则同样适用于有限元计算结果。
与Porowski模型类似,Dai等[21]在采用夹心梁模型[70]分析内壁变形时提出了基于内壁薄化量和变形极限的失效准则,其贡献是将传统的逐循环分析改为连续时域动态损伤计算,实时预测剩余寿命,配合发动机减损控制。如文献[79-82]建立了冷却夹套隔片的结构损伤模型,仿真发动机动态系统性能对损伤发展的影响,指出该模型还需更多借鉴材料、结构和损伤力学的方法,完善损伤动力学模型以进一步研究部件失效机理。Sung等同时采用基于塑性失稳的Porowski的矩形梁模型、文献[21]的夹芯梁模型和基于应变幅-寿命关系的有限元模型计算内壁寿命,表明采用黏塑性本构的夹芯梁模型对寿命预测效果较好[77-78]。从损伤准则来看,文献[21]的模型实质上是仅考虑变形极限而忽略低周疲劳和蠕变的Porowski模型,因而其对损伤机制的描述并不完善。但其时域连续损伤的概念及减损控制的思想对发动机健康监测和动态控制具有借鉴意义。
德国DLR的Riccius基于延性耗竭思想定义了准静态疲劳(棘轮)损伤[31],即循环载荷下的累积残余拉应变,该定义与Porowski模型的塑性失稳所关注的失效机理相似,但Riccius从塑性耗散的角度明确失效本质,并采用唯象学的复合损伤方法将准静态疲劳和低周疲劳叠加,正确定位了结构失效点-内壁中心[29-31]。该模型目前被众多学者采用,如Ferraiuolo等采用了Riccius评估内壁寿命,验证“狗室”失效特征[84]; 王召等分析了某甲烷发动机6种推力室方案中内壁材料、热处理状态、厚度、沟槽结构和涂层对寿命的影响[48]; 北京航空航天大学的康玉东等[50-51]采用Riccius模型分析不同内壁材料、厚度、高宽比推力室的低周和棘轮损伤,并将方法扩展为三维模型[52]。
CDM模型将材料性能衰退过程在响应分析和寿命预测中予以考虑,以损伤值阈值作为材料失效判据,其核心工作是损伤本构的建立和参数识别。从目前公开文献来看,CDM模型对结构失效形态的仿真效果较好,但寿命预测效果还需要更多验证。如Thiede等[34-35]在Tini等[32-33]的工作基础上建立了耦合Lemaitre各向同性损伤的Chaboche黏塑性本构模型,并引入材料老化影响。模型采用不同温度下的单轴拉伸试验标定材料硬化、蠕变和老化特性,复现了损伤发生点及肋的增厚现象,但无法反映冷却通道内壁的“颈缩”现象[见图7(a)]。后续工作引入裂纹闭合参数表征拉/压状态下等效杨氏模量的差异,成功描述“狗室”变形及疲劳寿命[36]。
此外,Schwarz等的三维热-结构分析结果很好地描述了内壁薄化现象并定量表征了“狗室”变形程度[见图7(b)][86]。研究表明失效与延性断裂相关; 不含损伤的模型严重高估了内壁寿命(3倍),而引入损伤后的仿真寿命仅比试验值高25%。文献[86]认为,考虑化学冲击和侵蚀作用或可更好地反映内壁薄化过程并得出偏保守的寿命预估[见图7(c)]。随后Schwarz分别采用各向同性和各向异性损伤模型对比微缺陷闭合效应对模型响应的影响,发现各向异性损伤和微缺陷闭合效应会增强燃气侧内壁的膨胀和薄化特征,但对总体失效行为的影响不显著[87]。若分析目的是获得失效位置和寿命,则无微缺陷闭合效应的各向同性损伤模型即可满足精度要求。
图7 CDM计算结果[34,86]
Fig.7 Results of CDM[34,86]
在最新的研究中,文献[88-89]基于Kowollik[63]建立了Astrium GmbH氢氧发动机推力室三维瞬态流-固耦合模型[见图8(a)],研究了内壁粗糙度、裂纹随循环的变化过程及热障涂层对结构工作状态的影响,同时基于已有黏塑性损伤模型[63]分析了疲劳寿命。目前来看,该研究对推力室结构的失效过程仿真最贴近试验现象,模型中最大损伤分布与失效试件外表面吻合,但仍未能准确表征内壁的薄化现象[见图8(b)]。
图8 CDM计算结果[63,88]
Fig.8 Calculated results of CDM[63,88]
从已有试验和仿真研究结果来看,推力室收扩段喉部的再生冷却结构是寿命薄弱点,其温度及压力场均匀但瞬时载荷突出。而重复使用设计下的多次启动-关机、回收及变推力工况增加了载荷的动态不确定性,在线损伤监测具有重要意义。
从国内工程需求来看,发动机重复使用寿命评估方法和标准尚未完善。各型发动机推力室的工况、内壁结构、材料性能、制造工艺存在差异,而“狗室”失效、蠕变损伤、基体/涂镀层耦合失效等问题均与实际结构和系统参数相关,且受材料制备和制造工艺影响,不能完全照搬国外研究经验。以蠕变损伤为例,其在内壁失效中的影响至今未有定论:Kasper研究表明蠕变影响显著,循环-蠕变寿命是低周疲劳寿命的30%~50%[44]; Armstrong等[38]、日本JAXA[85, 100-101]、Asraff等[91]均认为制约内壁寿命的主要损伤模式为低周疲劳损伤,其次为棘轮损伤,蠕变损伤贡献比低周损伤小2~3个数量级。在我国研制的各型号发动机中,内壁失效究竟与何种损伤密切相关,蠕变是否为重点考虑对象,采用何种本构关系和寿命模型等问题,都需要设计单位从基础数据和方法出发,系统、完整地建立寿命分析方法后才能回答。
结合目前研究进展和工程需求,可从以下方向开展研究。
变温环境下材料性能随温度动态变化,细微的温度偏差将导致结构力学响应和疲劳性能的显著差异[15],低温液体火箭发动机推力室分析中40 ℃的温度误差可能导致50%的寿命差距[23, 28]。因此精确的温度场是结构响应分析和寿命评估的关键。
启动、关机过程的热冲击和瞬态压力导致结构高速率热应变和机械应变,而铜合金具有显著的应变率敏感特性[38, 86],表现为率相关的屈服强度和硬化特性。忽略动态加卸载历程将使结构响应和疲劳寿命产生较大差异,已有研究表明瞬态分析下的最大残余应变比稳态分析高15.7%[61],结构寿命降低40%以上[31]。而引入瞬态载荷可更好地考虑热/压力冲击造成的结构损伤。此外,无显著冲击效应的动态瞬态也可能造成结构损伤,发动机完全关机不是非稳态热状态计算的结束时刻,温度载荷与响应的计算需要延续到关键区域温度场达到平衡状态为止。
目前,推力室内壁多采用单次稳态载荷曲线,除无法反映瞬态效应外,也不能包括影响重复使用发动机推力室疲劳寿命的全部工况。因此需要分析获得考虑推力室制造、考核试车、多次启动-关机、回收及变推力工况的全服役周期瞬态载荷环境。
推力室内壁工作于热-机械载荷下,本构关系需能反映变温下的材料性能变化、循环载荷下的等向/随动强化特性、非对称循环下的棘轮变形行为、高温下的蠕变现象及应变率敏感特征。目前尚未有通用的黏塑性本构关系可以完美描述各类材料的所有力学特性,需要针对材料特点、失效形式、应用场景和数据基础发展合适的本构关系。Arnold等在研究中发现,被广泛推崇的Robinson本构对内壁的薄化效应描述不足,而简单的幂律模型可以更精确且高效地模拟“狗室”效应[22]。Ferraiuolo等曾对比几类常用黏塑性本构对内壁变形的仿真结果,指出差异不大于10%,该结论普适性虽有待商榷,但一定程度上说明一味追求复杂的先进方法并不一定能显著提升分析精度[83]。
此外,应重视材料数据对参数标定的影响,试验数据的缺乏和参数识别的误差很容易掩盖复杂本构所带来的优势,甚至造成更大偏差。NASA早期研究就曾因试验数据缺乏而产生响应计算和疲劳特性插值的误差[38]。目前国内亟需完善与内壁实际加工制造过程、热处理工艺相一致的材料在不同温度下的基础力学参数、循环应力-应变特性及低周疲劳、蠕变和热-机械疲劳性能数据库,为本构参数的精准识别和结构寿命预测提供数据基础。
重复使用液体火箭发动推力室的设计寿命量级低于一般机械结构,属于超低周范畴,但可靠性要求苛刻,因此其寿命预测精度极为重要。延性损伤模型比Manson-Coffin等低周疲劳方法更适用于超低周疲劳分析[28],且可实时动态计算工作循环内的损伤发展情况,结合测量数据完成健康监测。结合目前国际前沿研究进展,可建立综合考虑延性耗竭、长时热效应、老化、化学作用的热-机械连续损伤模型(CDM),国内目前鲜有基于CDM的响应分析和寿命预测研究。
损伤模型的参数识别和可行性验证必须通过相关试验完成,而整机试车代价高、周期长且限于结构原因难以测量危险点的热/力学数据。可开展模块化推力室缩尺试验和热-机械模拟件试验,通过实时测量、结构无损检测和断口分析等手段明晰内壁损伤机理、建立并验证损伤模型。除此之外,还可开展发射回收后发动机推力室的损伤检测技术,量化结构失效特征,验证数值分析方法并评估推力室剩余寿命。
目前液体火箭发动机推力室内壁普遍采用涂/镀层工艺达成隔热、防氧化、抗腐蚀的目的。涂/镀层的表面状态变化、局部破损、翘曲和脱落将改变壁面流动换热及内壁热载荷,进而影响结构寿命。目前氢氧发动机一般采用热障涂层,其损伤及剥落对内壁热载荷的影响大于结构影响; 而液氧煤油发动机一般采用Ni/Cr厚镀层,硬质镀层与内壁厚度相当,其在结构强度上的贡献和疲劳寿命中的作用不容忽视; 镀层和内壁间存在力学响应失配和损伤发展不同步,二者的耦合作用可能导致多种潜在失效模式,而国内外鲜有相关研究。为合理评估内壁的整体失效,需建立基体与涂/镀层耦合失效模型。
实际工程设计中,设计人员往往仅能获得有限的载荷特征和材料试验数据,先进方法的适用性和可靠性难以保证[102]。我国液体火箭发动机型号多,结构设计、系统参数、载荷工况和制造工艺差异大,逐型号获得系统完整的载荷环境、材料本构关系、性能数据库和先进寿命分析方法需要长期的科研与试验投入。考虑到目前重复使用的紧迫需求,设计人员短期内将面临基于少量数据的参数标定、不完全载荷特征下的寿命评估和基于等温疲劳数据的热-机械失效分析等问题,而建立基于有限数据的工程方法具有重要意义。
本文综述了重复使用液体火箭发动机再生冷却推力室内壁的热-机械疲劳分析方法,介绍其发展历程并对比梳理了主要方法和代表性研究,最后给出研究建议:为发展先进方法,可分析获得全服役周期瞬态载荷环境,建立精确的材料本构关系、热-机械损伤模型并考虑基体与涂/镀层的耦合失效行为; 从短期工程需求考虑,应建立基于有限数据的工程分析方法。