基金项目:国家科技重大专项(J2019-IV-0014-0082); 国家级青年人才项目; 江苏高校优势学科建设工程资助项目
作者简介:孙燊(1998—),男,博士,研究领域为疲劳断裂相场理论模型及计算。
通信作者:易敏(1987—),男,博士,教授,研究领域为先进材料与结构力学。
State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control for Aerospace Structures,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and AstronauticsNUAA, Nanjing 210016, China
regeneratively cooled thrust chamber; thermal mechanical fatigue; fracture; phase field; life prediction
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9374.2024.01.007
可重复使用运载器具有高效、经济、环保等特点,是目前航天技术发展的重要方向[1]。2015年以来,美国私人航天公司SpaceX回收并重复使用猎鹰9号运载火箭,国外研究机构不断突破,以求摆脱单次使用运载火箭高昂费用对空间探索的制约。我国一方面密切追踪国外先进技术发展[2-3],另一方面努力推进自身关键技术攻关。可重复使用运载器技术既能降低空间运输成本,贯彻可持续发展战略,又是彰显综合国力、抢占空间优势的必要工具。液体火箭发动机作为动力装置,其耐久性和可靠性是保障运载器可重复使用的关键。推力室喉部结构是液体火箭发动机的核心部件,在服役过程中会经历复杂、交变的热机载荷作用,不均匀的温度分布、局部的塑性应变更会加快结构的疲劳失效。因此,对推力室喉部结构进行传热分析和疲劳寿命预测具有重要意义。
推力室在工作时会经历急速的升温与降温,在局部会发生较大的热变形,分析结构承受的热载荷需要计算结构的传热情况和温度分布。推力室内壁需要承受高温燃气的冲刷作用,冷却剂在冷却通道中逆流降温。多种材料分别具有不同的物性,对传热分析的计算结果提出很高的要求。吴峰等应用湍流模型进行了三维数值模拟,计算了再生冷却推力室通道的流动与传热[4]。韩炜对推力室的再生冷却情况进行了三维数值模拟,得到了内壁面上温度分布一般规律[5]。吴有亮等提出了推力室准二维传热计算的通用方法,相较于三维计算,降低了计算时间,极大地提升了计算效率[6]。根据传热分析得到的温度分布可以计算结构中的热本征应变,可仿真模拟燃气温度和燃气压强载荷的共同作用效果,并预估推力室使用寿命。孙冰等对推力室结构进行了三维瞬态热分析,并根据应力应变分布预测了结构危险点的失效情况[7-9]。徐绍桐等建立了推力室壁在燃气/冷却液温度和燃气压强载荷下的二维弹塑性计算模型,提高了失效行为模拟的计算速度[10]。张明等通过数值计算研究了变截面冷却通道的传热情况[11]。目前,推力室疲劳寿命预测的研究主要是基于损伤力学计算损伤的累积,或者根据应力-应变法计算材料的疲劳寿命,较少从断裂力学出发预测寿命。
传统方法处理断裂问题往往将界面作为一个突变的量来处理,突变问题的数值奇异性增加了问题的求解难度。在材料断裂的界面,数值上难以进行微分算法,材料参数需要考虑因材料破坏而损失的刚度。相场模型通过引入在界面处急剧变化但连续的相场变量——序参量来描述不同的相[12-14],断裂序参量在整个计算区域上是连续变化的,因此相场模型中不再需要采用特殊的数学方法追踪界面的几何形态,也避免了追踪断裂面所引起的误差。相场断裂方法可以反映加载过程中断裂序参量的演化,直观地观察到裂纹的演化。Francfort等[15]通过对Griffith断裂理论[16]及变分公式的研究,提出了准静态脆性断裂的相场模型。Miehe等提出了应变张量的谱分解方法,用以区分压缩和拉伸对应的应变能,并且推广到热-弹-塑性耦合的断裂问题[17-19]。文献[20-21]通过修正断裂相场模型中的断裂韧性,实现对疲劳断裂问题的相场模拟。
本文使用相场疲劳断裂模型对再生冷却推力室喉部结构进行有限元模拟,通过热传导方程考虑温度载荷引入的热本征应变,得到结构的温度和应力/应变分布情况,根据相场序参量的变化分析结构的疲劳断裂过程,研究推力室结构在服役过程中的失效行为和热机疲劳寿命。
铣槽式再生冷却推力室采用等肋宽的薄壁结构,其喉部自内向外分别为内壁、冷却通道和外壁,冷却通道使用肋片进行强化传热。推力室中实际发生的热量传递包括:燃气对内壁的加热、冷却剂对冷却通道的对流换热。考虑热载荷对受力的单向耦合,采用稳态热平衡方程对温度场进行传热分析,热传导的控制方程为无热源的导热微分方程,即
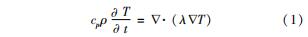
式中:cp为定压比热容; ρ为材料密度; T为结构温度; t为时间; ▽为哈密顿算子; λ为材料热导率。
发动机推力室在工作过程中同时受到温度载荷和机械载荷的作用。结构的总应变εtotal由热应变εth、弹性应变εela、塑性应变εpla和蠕变应变εcr构成,即
εtotal=εth+εela+εpla+εcr (2)
热应变与温度的变化成线性关系,即
εth=αthΔTI (3)
式中:αth为线膨胀系数; ΔT为相对参考温度的温度变化量; I为二阶单位张量。
在分离弹性应变和塑性应变时,使用von Mises屈服准则来判断材料是否达到屈服,屈服条件表达式为
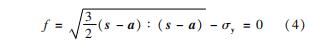
式中:f为屈服函数; s为偏应力张量; a为背应力张量,即屈服面中心; σy为屈服应力。
达到屈服面后塑性应变产生,塑性应变沿着屈服面梯度方向增加,即
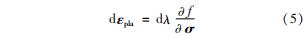
式中:dλ为塑性乘子,即等效塑性应变增量; σ为应力张量。
计算蠕变应变时,考虑陈化理论,即Norton定律。在蠕变过程中,时效、扩散和恢复等因素影响蠕变行为,其中时间是最大的影响因素。Norton模型的表达式为
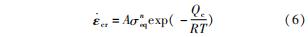
式中:ε·cr为蠕变速率; A为材料蠕变常数; σeq为Mises等效应力; n为蠕变指数; Qc为蠕变激活能; R为气体常数。蠕变本构主要影响结构的应变构成,进而影响弹性应变和裂纹扩展的弹性应变驱动力。本文暂未考虑蠕变对材料断裂韧性的影响。
定义相场序参量c表示材料的断裂情况,如果材料完好未损坏,则c为 1; 如果存在裂纹,则c为 0。因此,变量c可以看作是损伤力学模型中的损伤参数。断裂模型中总自由能密度由弹性应变能、塑性应变能和断裂界面能组成,表达式为
ψ=ψela+(1-c)2ψpla+ψc (7)
假定弹性应变中只有拉伸分量驱动裂纹扩展,将弹性应变谱分解为
εela=PΛPT (8)
式中:Λ=diag(λ1,λ2,λ3)是与弹性应变张量相似的对角阵,λ1、λ2、λ3为弹性应变的特征值; P为特征矩阵。
根据谱分解,弹性应变的正负分量为
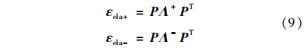
弹性应变能密度分解为驱动裂纹扩展的拉伸部分ψela+和不可驱动裂纹扩展的压缩部分ψela-,表达式为
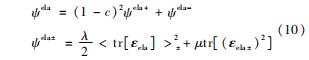
根据Borden的塑性断裂相场模型[22],塑性应变能密度表达式为
ψpla=∫σdεpla (11)
裂纹的相场演化方程表示为
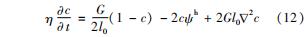
式中:η为动力学系数; l0为界面宽度尺寸; G为临界断裂能密度; ψh为驱动裂纹扩展的历史变量,即
ψh=maxt[ψela+(εela)]+ψpla(εpla) (13)
推力室结构在工作过程中会经历周期性的热应力或热应变,单次循环载荷作用下,应力水平可能远低于使材料断裂的临界应力,但是仍会经历往复循环的塑性变形。因此,需要考虑循环载荷下的相场疲劳断裂模型。通过引入疲劳退化函数,对材料的断裂韧性进行修正,使其在循环载荷下不断衰减,模拟结构在疲劳载荷下的断裂失效。采用的退化函数为
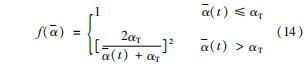
式中:αT为疲劳阈值;(-overα)(t)为疲劳累积函数,用来计算历史变量α=‖εela+εpla‖的累积,累积函数表达式为
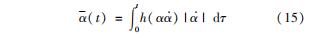
h(α(·overα))为符号函数,定义为
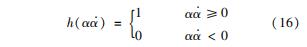
疲劳断裂的相场演化方程表示为
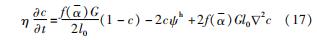
推力室喉部为环形对称结构,选取1/2冷却再生通道截面作为计算模型,结构的几何特征与边界条件如图1所示。
本文在 MOOSE(Multiphysics Object-Oriented Simulation Environment)框架下进行模拟,通过编写有限元程序,利用PETSc求解器和Libmesh库进行并行计算。为了提高计算效率,使用二维平面应变结构进行模拟。本文采用四边形网格进行网格划分。模型网格基础尺寸为0.1 mm,在肋片和内壁进行加密,尺寸最小为0.01 mm,网格数量为16 305。对于网格无关性验证,进行了6 495、16 305和29 888不同单元数量的测试,3种网格的温度分布基本一致,第一种网格与后两种网格所获得的应力/应变分布有明显差别,后两种网格所获得的结果基本一致,故本文结果皆是基于第二种网格(16 305单元)得到的。计算采用单向耦合求解,在每一个时间步,先进行传热计算,得到温度分布后,将温度转化为热应变,代入力学方程求解应力/应变和断裂相场值,然后进行下一时间步的计算。模型的两边设置为对称边界。发动机工作过程分为启动-热试车-后冷-关机4个阶段,各阶段时长分别为5、300、20、600 s,环境温度为295.15 K。结构的温度边界条件和压力边界条件参见文献[23]。
结构的内壁和肋片材料为NARloy-Z铜合金,外壁材料为1Cr21Ni5Ti。NARloy-Z铜合金性能参数参照Esposito 在高低温环境下的单轴拉伸试验数据[24],蠕变模型使用Ellis得到的不同温度、不同应力水平下的蠕变试验数据[25]。相场疲劳断裂模型的参数见表1。为了获得相场模型参数,根据材料的屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率等参数先进行不同参数下的单轴拉伸计算测试,选取能实现吻合实验结果的模型参数,再进行推力室受载计算。
不同阶段下结构的温度分布如图2所示。在热试车阶段,结构的升温比较明显,最高温度出现在内壁下表面,G点温度最高可达881.17 K。
选取结构上7个参考点的温度变化曲线,如图3所示。可以看出:自下而上,内壁温度最高,肋片次之,外壁温度最低。由于内壁与肋片的材料热导率高于外壁,外壁上参考点的升温速率也明显慢于其他两部分。外壁上B、C两点的温度基本一致。
推力室单次工作各阶段结构的应力/应变分布如图4和图5所示。在开机阶段,结构升温幅度较小,整体的压应力和压应变的数值较低。由于肋片膨胀受到内、外壁的限制,整体处于压应力水平。在热试车阶段,结构整体升温,受热膨胀,由于受到对称边界的限制,结构整体表现为受压。肋片膨胀受到外壁限制,C处会产生较高的压力。该阶段下,结构内壁下表面温度最高,G点受到左侧边界的限制,受到的压应变最大,最高达到1.34%。在后冷阶段,结构弹性变形恢复,内壁由于压载较大,降温后有残余的塑性变形。内壁下表面F点和G点分别表现为残余拉应变和残余压应变。F点受到拉伸载荷,残余应变约为1%。在关机阶段,结构的温度分布与后冷阶段相差不大,结构最终的受载情况和残余应变与后冷阶段基本一致。
根据应力和应变分布图,确定D、E、F、G这4点在工作过程中受到的局部应力-应变较大,为服役危险点。这4点的应力、应变曲线如图6所示。4个点在循环中都经历压应力变为拉应力,D、E、G点始终受到压应变,F点最终由压应变转变为拉应变。
对10个工作循环下的推力室喉部结构进行仿真。根据单次循环应力应变分析,结构的危险点位于内壁下表面的F和G点,循环仿真后重点关注F和G点的应力应变情况。F点和G点10次循环的应力应变曲线分别如图7和图8所示。随着循环数的增加,F、G两点表现为应力控制的非对称循环加载,并且每次循环结束残余应变值不断增加。其中,F点为拉伸应变,G点为压缩应变。F、G两点残余应变发展曲线如图9所示。
由于单次循环结构承受的最大应力小于材料断裂破坏的临界应力,结构中的断裂序参量增长较小。循环加载并计算结构的断裂序参量,直至结构中出现序参量值达到0.95则停止计算。最终发现,91个循环后结构失效,计算停止,F点断裂序参量最先达到临界值c=0.95,表明结构的疲劳寿命为91次循环,失效点位于内壁下表面F点。
单次循环后的序参量分布如图 10所示。图 10表明,结构中内壁下表面中心点F序参量最大,在单次工作结束后,F点的损伤最大,但此时序参量的值还处于很低的水平,对结构的承载能力影响不大,不会使应力衰减,仍可以进行多次循环工作。结构在内壁下表面受到的温度载荷最高,并且F点由于对称边界受到约束,在温度恢复常温后,受到的拉应力最大,所以序参量演化最快。根据应力分布云图,在结构变截面处,即C、D点会出现应力集中。C点受到的温度载荷较低,所以温度载荷恢复后受到的载荷水平较低,没有出现损伤。D点受到的温度载荷较高,相场值为6×10-7,但与F点相比仍较低,因此结构并未在变截面处出现裂纹。
10次循环后的序参量分布如图 11所示,结果与单次循环相似,仍在F点序参量值最高。
结构中的断裂序参量演化如图 12所示。随着循环数增加,下表面的断裂序参量值不断上升,并且EF边界明显快于内壁其他区域,从F点到E点从大到小基本呈线性分布。
结构失效破坏时的径向位移如图 13所示。疲劳破坏时,EF边界明显向下凹陷,内壁不断变薄,最终在F点处断裂失效。
本文采用热-弹-塑性耦合的疲劳断裂相场模型,分析了火箭发动机再生冷却推力室结构在循环运行过程中的温度、应力和应变分布及变化,根据断裂序参量的演化,分析了热机疲劳破坏行为并计算了结构的疲劳寿命,主要结论如下。
1)推力室结构在工作过程中热量自下而上传导,温度逐渐降低。结构升温降温产生的塑性变形是导致结构疲劳失效的主要因素。
2)结构内壁部分变形较大,随着循环次数增加,F点和G点分别不断累积残余正应变和残余压应变。
3)F点受到残余正应变积累,驱动裂纹扩张的拉伸应变能不断增加,最终导致结构发生疲劳破坏。内壁中心受到残余正应变,使内壁向下表面塌陷,壁面变薄。