基金项目:国家重点实验室基金项目(2023LB013006); 中国航天科技集团有限公司自主研发项目
作者简介:苏鹏程(1998—),男,硕士,研究领域为金属疲劳与本构、增材制造技术。
通信作者:王佩艳(1984—),女,副教授,研究方向为金属和复合材料失效。
1.西北工业大学 力学与土木建筑学院,陕西 西安 710129; 2.航天液体动力全国重点实验室,陕西 西安 710100
1.School of Mechanics, Civil Engineering and Architecture, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710129, China; 2.National Key Laboratory of Aerospace Liquid Propulsion, Xi'an 710100, China
nickel-based superalloy; constitutive model; rheological behavior; laser additive manufacturing; finite element simulation
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9374.2024.01.013
镍基高温合金是一种在高温条件下具有高的拉伸强度和蠕变强度,具有良好的抗氧化、抗燃气腐蚀能力等优异性能的高温合金,被广泛应用于航空航天、船舶制造、汽车领域等发动机中的热端部件[1]。采用传统制造方法加工镍基高温合金构件无法满足复杂结构一体化成型的要求。近年来,增材制造技术作为一种直接成型制造技术,已经发展为先进制造领域的新兴高端技术,能满足真正的“自由制造”需求[2-3]。增材制造(3D打印)技术一方面可实现复杂航天产品的制造,如航天发动机推力室、涡轮泵及阀门、总装及其他元件、发动机整机等产品的整体化、轻量化制造,另一方面能降低生产成本和缩短研制周期,因此极大地推动了航天事业的发展[4-7]。综合镍基高温合金和增材制造的优势,有必要开展增材制造镍基高温合金的应用研究。
为了探究增材制造镍基高温合金在不同温度下的变形能力,需要开展相应温度条件下的拉伸试验。高温合金的塑性变形行为是一个非常复杂的过程,应变、应变率和温度等试验参数会影响高温合金的硬化或软化机制[8]。高温合金在不同温度下的流动应力是描述材料变形过程重要的性能指标之一,是加工硬化、动态回复和动态再结晶过程的反映[9]。目前,已经有多种描述塑性行为的本构方程被开发,用以预测高温合金在不同试验条件下的流动应力。高温合金本构模型可分为唯象模型[10](经验模型)、物理模型[11]、人工神经网络模型[12]等。
唯象模型旨在利用形式简单且参数少的方程式来描述材料复杂的塑性变形行为,工程应用较为方便[13]。在唯象模型方面,Johnson-Cook(J-C)模型参数少,公式简单,且兼顾温度和应变率效应,因此工程应用最为广泛。J-C模型同样被嵌入多种大型商业有限元软件中,然而,J-C模型不能描述各种材料及载荷状态下的屈服现象和应力流动[14]。Lin等提出了考虑应变、应变速率和变形温度耦合效应的改进J-C模型来描述所研究合金钢的拉伸行为,结果表明,该模型预测的应力应变值与试验值吻合较好[15]。Zhang等通过引入温度效应函数,对J-C模型进行改进,并用于预测IC10在不同实验条件下的流动行为,结果表明该方法是有效的[16]。
在物理模型方面,Zerilli等考虑了微观组织对塑性变形的影响并基于金属位错力学理论推导出Z-A本构模型,充分考虑了应变、温度和应变率对塑性变形的综合影响[17]; Zhang等考虑了应变、温度及应变率对本构模型参数的耦合影响,在Z-A模型基础上对其进行了改进,改进后的模型可以更好地描述IC10的塑性流动行为[18]; Samantaray等参考了J-C模型的函数形式,以此为基础对Z-A模型进行修正,得到的修正模型能更好地预测D9的塑性流动应力[19]。
综上所述,唯象模型形式简洁、规律直观; 物理模型考虑了塑性变形的物理机制,其参数具有特定的物理意义。因此,本文开展了激光增材制造镍基高温合金在7种温度下的拉伸试验,考虑应变硬化和温度软化对镍基高温合金塑性行为的耦合影响,分别提出了以J-C唯象模型和Z-A物理模型为基础的改进本构模型预测镍基高温合金在-150~600 ℃范围内的塑性流动行为; 利用有限元分析软件对拉伸试验进行模拟,以此来验证所提出的改进本构模型的准确性。
试验用增材制造镍基高温合金采用选择性激光熔化技术(SLM),试样取样方向沿着增材制造的沉积方向。
增材制造镍基高温合金的室温(25 ℃)、高温(200、300、400、500、600 ℃)和低温(-150 ℃)拉伸试验按照GB/T 228.1—2010《金属材料拉伸试验第1部分:室温试验方法》、GB/T 228.2—2015《金属材料 拉伸试验 第2部分:高温试验方法》和GB/T 228.3—2019《金属材料 拉伸试验 第3部分:低温试验方法》标准在100 kN电子万能试验机上进行。进行高温试验时,根据试验温度准备相应的环境箱或高温炉,调试温度,待温度达到指定温度后保温20 min,确保试件均匀受热后开始试验; 进行低温试验时,利用液氮调试温度,待温度达到指定温度后保温20 min进行试验。利用位移控制试验的进程,直至试件破坏,拉伸破坏断口位于试件工作段时认为试验有效; 每个温度下进行10次试验,以确保试验结果的重复性。
拉伸试验件尺寸(单位:mm)和试验件加载方式如图1所示。
由于在拉伸过程中试件的长度和截面积不断变化,工程应力和工程应变不能准确反映材料变形过程中的真实应力和真实应变。因此,应将工程应力和工程应变转化为真实应力和真实应变,用以计算屈服强度及抗拉强度。
对不同温度下的原始数据进行处理,得到镍基高温合金的真实应力-应变曲线,各个温度下基本力学性能数据的平均值如表1所示。
图2绘制了不同温度下的屈服强度σs、抗拉强度σb、断后伸长率δ和断面收缩率ψ的误差棒图。
从图2可看出:屈服强度和抗拉强度的大小随着温度的升高而减小; 断后伸长率随着温度的升高上下波动,峰值出现在123 K,波动可能是动态应变时效所引起的; 断面收缩率整体上随着温度的升高而增大。123 K温度下增材制造镍基高温合金的断后伸长率大,断面收缩率小,这是因为试件在整个标距段内都有塑性变形,而颈缩不明显。结果表明,镍基高温合金在低温时具有良好的力学性能。
从各个温度下的数据中各挑选一组与平均值结果相近的真实应力-应变数据进行分析。图3显示了不同温度下所分析试样的单轴拉伸试验颈缩前屈服阶段的真实应力-应变响应。
图3 镍基高温合金在不同温度下颈缩前的屈服阶段真实应力-应变曲线
Fig.3 True stress-strain curves of Nickel-based superalloy at different temperatures before necking
从图3可看出,流动应力整体上随温度的升高而降低。这是由于随着温度的升高,温度对材料变形的软化作用增大,流动应力相应减小。
当试验温度为673 K、773 K和873 K时,材料在达到临界塑性应变后,流动应力的塑性变形阶段出现了锯齿流变现象。Chihab等根据形态将锯齿型分为A型、B型和C型3种[20]。A型锯齿波一般出现在较低的温度和较小的应变量条件下,B型和C型锯齿波一般出现在较高的温度和较低的应变速率下[21]。本研究所观察到的锯齿型仅有B型和C型两种,如图3中局部放大图所示,673 K和773 K时的锯齿型称为B型,873 K时的锯齿型称为C型。锯齿流变现象的发生,一方面是由于镍基高温合金内部扩散的溶质原子和移动位错之间相互作用的结果,可以用动态应变时效(Dynamic Strain Aging,DSA)机制来解释[22-23],根据DSA的扩散控制模型,锯齿的出现需要激活能量,即溶质迁移需要能量,高温作用下给溶质原子提供了足够的能量以摆脱位错; 另一方面在较低的应变加载速率下,合金内部位错的动能较小,孪晶界可有效阻止位错的滑移,从而导致位错的堆积和严重的应力累积,当应力积累到一定阈值时,位错会穿过孪晶界,以释放积累的内应力,从而在应力-应变曲线上出现上升和下降的应力波动,即锯齿流变行为[24]。因此,DSA理论和基于位错的运动理论可共同解释高温下镍基高温合金中出现的锯齿流变现象。
基于以上分析,在同等应变速率下,出现B型锯齿的原因可能是在扩散的溶质原子和移动位错相互竞争作用中,位错的运动占据主导地位,因此会出现大量的位错堆积和滑移,导致应力累积和释放,在应力-应变曲线上表现为连续且均匀的上升和下降的应力波动; 出现C型锯齿的原因可能是溶质原子的扩散和移动位错相互竞争过程中,溶质原子的扩散占据主导地位,且在更高的温度下,溶质原子的扩散更加容易,因此在应力-应变曲线上表现为间断且少量的应力波动。
许多研究表明,高温合金流动应力随温度的增大并不是逐渐减小,有时会出现流动应力随温度升高先减小后增大再减小的反常现象,该现象被命名为第三型应变时效[25-29]。为分析同一应变下温度对材料拉伸真实应力的影响,可随机取几个不同应变数据点,基于所选的应变点,得到温度对拉伸真实应力的影响如图4所示。
图4 镍基高温合金在同一应变下拉伸真实应力随温度变化趋势
Fig.4 Variation trend of true tensile stress with temperature change under the same strain for Nickel-based superalloy
从图4可看出:在相同应变下,拉伸真实应力整体上随着温度的升高而减小,说明具有温度效应; 温度大于773 K时,曲线趋于水平且个别应变下的曲线略有上升趋势,说明此时可能出现第三型应变时效; 另外,低温时不同应变所对应真实应力的差值大于高温时不同应变所对应真实应力的差值,此现象说明镍基高温合金在低温时应变硬化现象更加明显。
在唯象本构模型中,J-C模型成功地应用于描述很多铝合金和钢等金属材料在大变形、高温和高应变速率下的流变行为,且模型公式简单,材料常数少,工程应用较为方便[30]。J-C模型一般表达式为[31]
σ=(A+Bεn)(1+Cln ε·*)[1-(T*)m] (1)
式中:σ为等效流动应力; A为参考温度和参考应变率下的屈服应力; B为应变硬化系数; n为材料的应变硬化指数; ε为等效塑性应变; C为应变率硬化系数; m为温度软化指数; ε·*为无量纲应变率比值,表达式为
ε·*=ε·/ε·0 (2)
式中:ε·为应变率; ε·0为参考应变率。
T*可表示为
T*=(T-Tr)/(Tm-Tr) (3)
式中:T为绝对温度; Tr为参考温度; Tm为熔化温度。
利用试验所得真实应力-应变数据拟合原始J-C模型的参数,试验考虑了温度的影响,未考虑应变率,因此式(1)中未考虑第2项。
在不同参考温度下(123 K和298 K)拟合原始J-C模型参数,拟合的模型参数具体值如表2所示。
所得不同参考温度下原始J-C模型表达式为
σ=(1 356.8+1 306.9ε0.539)[1-(T*)2.08] (4)
σ=(1 278.5+884ε0.453)[1-(T*)2.11] (5)
不同参考温度下原始J-C模型所拟合的流动应力值与试验流动应力值的对比如图6所示,当Tr=298 K时,原始J-C模型不能拟合出123 K时的流动应力曲线,这是因为当T=123 K时,T*为负,此时不能拟合出流动应力。
图6 原始J-C模型拟合流动应力值与试验值对比
Fig.6 Comparison of flow stress values fitted by the original J-C model with experimental values
从图6可看出:只有在参考温度下,原始J-C模型的预测值与试验值吻合较好,在其他温度下预测值与试验值相差较大,原因在于试验所得屈服以后的流动应力随着温度升高变化率越来越小,因此流动应力-应变曲线斜率越来越小。而原始J-C模型应变硬化项的参数是基于参考温度下的试验数据所拟合,温度软化项等同于一个常数,曲线的斜率不会发生改变,因此原始J-C模型拟合不同温度下的流动应力-应变曲线相当于将参考温度下的曲线进行上下平移。平移量根据温度软化项确定,仅与温度差值相关,没有考虑该温度下真实的屈服强度值。因此,原始J-C模型不能直接用来拟合镍基高温合金的流动应力,而需进一步改进。
J-C模型认为应变硬化、应变率效应和温度效应对材料的流动行为的影响是相互独立的,因此在模型中是3部分的乘积。实际上,应考虑应变、应变率和温度对镍基高温合金塑性流动行为的耦合影响。
从图4可看出:在123~773 K的温度范围内,流动应力随着温度的升高而减小; 在773~873 K温度范围内,随着温度的升高,流动应力变化不大,甚至略有增加。这种异常的温度依赖性不能用原始J-C本构模型来描述,为了准确预测温度对镍基高温合金流动行为的影响,本文基于原始J-C本构,增加了应变和温度的耦合项,建立了基于原始J-C的改进模型,即
σ=Aexp(m'T*)+B(T*)εn (6)
式中:B(T*)为描述温度效应的T*函数; T*=T-Tr; m'为材料参数。式中第二项考虑应变和温度的耦合影响。
式(6)中包含的参数可通过以下步骤来确定。
1)参数A和n的确定。
当T=Tr(298 K)时,式(6)可写为
σ=A+B(T*)εn (7)
当ε=0时,等效流动应力为屈服应力,即σ=A=σ0.2r。对式(7)两边取对数得
ln(σ-A)=ln[B(T*)]+nln ε (8)
通过试验数据拟合得到ln(σ-A)-ln ε曲线,曲线的斜率为n。2)参数m的确定。
当ε=0时,有
σ0.2=Aexp(mT*) (9)
通过试验数据拟合σ0.2-T*曲线,即可求出m的值。
3)函数B(T*)的确定。
当A、n、m确定后,取ε=0,式(6)可写为
σ0.2=Aexp(mT*) (10)
当ε=εb时,等效流动应力为抗拉强度σb,式(6)简化为
σb=Aexp(mT*)+B(T*)εnb (11)
式(10)和式(11)联立可得
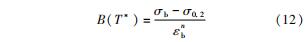
σb∝T*和εb∝T*的函数可以分别表示为
σb=σbrexp(lT*) (13)
εb=εbrexp(kT*) (14)
式中l、k为材料常数。
函数B(T*)的表达式为
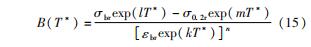
因此,以J-C模型为基础的改进本构模型的表达式为
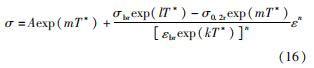
利用试验所得的真实应力、应变数据,按照式(16)拟合以J-C模型为基础的改进模型的参数,拟合结果如表3所示。
以J-C模型为基础的改进模型表达式为
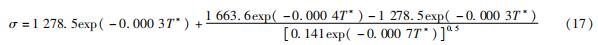
Zerilli等基于金属位错力学理论推导出Z-A本构模型,该模型既考虑了微观组织对塑性变形的影响,又研究了应变、温度和应变率对塑性流动行为的耦合影响[17]。Z-A本构模型将流动应力分为非热分量(σa)和热分量(σth)两部分。
σ=σa+σth (18)
根据不同的晶体结构,金属材料流动应力可表示为不同形式,如体心立方(Body-Centered Cubic,BCC)结构,Z-A本构模型表示为
σ=C0+C1exp(-C2T+C3Tln ε·)+C4εn (19)
针对面心立方(Face-Centered Cubic, FCC)结构,Z-A本构模型表示为
σ=C0+C1ε1/2exp(-C2T+C3Tln ε·) (20)
式中C0、C1、C2、C3、C4、n为材料系数,需要通过数据拟合获得。
从式(19)~式(20)可看出,结构中温度和应变率与应变项是相加的关系,FCC结构中应变率和温度项与应变项相乘,相比于BCC结构,FCC结构充分考虑了应变率和温度的耦合效应。
为了准确预测温度对镍基高温合金流动行为的影响,本文针对镍基高温合金的塑性流动行为,在面心立方Z-A模型的基础上,结合J-C模型的形式特点提出了改进模型,即
σ=(A+Bεn)exp[(C1+C2ε)(T-Tr)] (21)
式中:C1、C2为材料常数; A、B、n、ε、T、Tr的意义与原始J-C模型相同。
以Z-A模型为基础的改进模型中各参数项可通过以下步骤来确定。
1)参数A、B、n的确定
当T=Tr(298 K)时,式(21)可表示为
σ=A+Bεn (22)
由298 K下的真实应力、应变数据可得A的值,B、n可通过拟合该温度下的真实应力、应变数据确定。
2)参数C1、C2的确定
引入一个新的参数λ(λ=C1+C2ε),是应变的函数,则式(21)可表示为
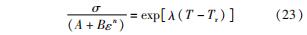
对式(22)两端取对数可得
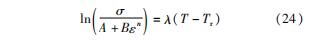
在不同温度和应变下,可以得到ln(σ/A+Bεn)和T-Tr的关系,最后,从λ-ε图中进行拟合可得C1、C2的值。
利用试验所得的真实应力、应变数据拟合改进本构模型的参数,参数拟合值如表4所示。
改进模型表达式为
σ=(1 278.5+884ε0.453)exp[(-0.000 255 2-0.000 876 7ε)(T-Tr)] (25)
采用以J-C和Z-A模型为基础的改进模型对激光增材制造镍基高温合金不同温度下的流动应力进行拟合,拟合结果与试验结果对比如图7所示。
图7 镍基高温合金在不同温度下流动应力的拟合值与试验值对比
Fig.7 Comparison of fitted and experimental values of flow stress at different temperatures for nickel-based superalloy
为定量分析这两种改进本构模型拟合结果的优劣,拟合流动应力σf与试验所得流动应力σe之间的相对误差,计算式为
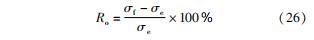
表5给出了镍基高温合金在不同温度下拟合流动应力与试验流动应力的对比和相对误差大小,可看出以J-C模型为基础的改进本构模型拟合最大相对误差为-3.0%,以Z-A模型为基础的改进本构模型拟合最大相对误差为-3.10%。结果表明,改进的本构模型能准确拟合镍基高温合金的流动应力。
利用Abaqus有限元分析软件对拉伸试验进行模拟分析,通过对比有限元和试验所得的载荷-位移曲线来验证所建立改进本构模型的正确性。由于试验是在不同温度下进行的,因此有限元分析时分析步类型为温度-位移耦合,以此来进行模拟计算。
在Abaqus中建立光滑圆棒的1/8模型用来分析计算,以此提高运算效率。对模型的3个对称面建立对称边界条件(U1=UR2=UR3=0,U2=UR1=UR3=0,U3=UR1=UR2=0); 将模型的夹持端侧面耦合到载荷施加参考点上,对参考点施加沿轴向的位移载荷,其他方向的自由度设为0,具体的施加方式如图8所示。
模型的整体网格尺寸为0.5 mm,为了提高计算精度和准确性,对模型的工作段进行加密处理,工作段的网格尺寸为0.2 mm,模型最终划分为21 505个单元类型为C3D8T的网格,网格划分结果如图9所示。
将不同温度下有限元分析与试验所得载荷-位移曲线进行对比,对比结果如图 10所示。
从有限元分析结果与试验的载荷-位移曲线对比可看出,两种改进本构模型均能较好地预测镍基高温合金的塑性流动行为。
为定量分析这两种本构模型预测结果的优劣,有限元分析结果和试验结果的相对误差可由式(26)计算,有限元结果与试验结果对比及相对误差如表6所示(其中Fe为试验拉伸载荷,Fp为预测拉伸载荷),从表6中可看出以J-C模型为基础的改进模型最大相对误差为-6.1%,以Z-A模型为基础的改进模型最大相对误差为-8.6%。结果表明,两种改进本构模型均能较好地预测镍基高温合金的塑性流动行为。
图 10 镍基高温合金在不同温度下有限元与试验载荷-位移曲线对比
Fig.10 Load-displacement curve comparison of finite element analysis and test under different temperatures for Nickel-based superalloy
本文对激光增材制造镍基高温合金在不同温度下进行了拉伸试验并对试验数据进行了处理,得到镍基高温合金的基本力学性能数据; 对某些温度下的试件断口进行SEM观测分析; 对试验数据拟合得到两种拟合镍基高温合金流动应力的改进本构模型; 利用有限元软件对拉伸试验进行模拟。
1)激光增材制造镍基高温合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度整体上随着温度的升高而降低; 断后伸长率随着温度的升高上下波动,123 K时的值最大,波动是动态应变时效效应所引起的; 断面收缩率整体上随着温度的升高而增大; 镍基高温合金在低温时具有良好的力学性能; 不同温度下试件断口表面存在大量韧窝和撕裂棱,具有明显的韧性断裂特征。
2)考虑了温度和应变对镍基高温合金塑性流动行为的耦合影响,分别建立了以J-C和Z-A模型为基础的改进本构模型来拟合镍基高温合金的流动应力,拟合最大相对误差分别为-3.0%和-3.10%,证明本构模型拟合结果和试验值吻合较好。将有限元分析结果和试验所得载荷-位移曲线进行对比,预测最大相对误差分别为-6.1%和-8.6%,对比结果均吻合较好,进一步证明了所建立本构模型的正确性。