基金项目:液体火箭发动机技术国家重点实验室基金(6142704220101); 陕西省自然科学基金青年项目(2024JC-YBQN-0535)
作者简介:彭乐钦(1989—),男,博士,研究领域为发动机流动燃烧与传热技术。
西安航天动力研究所 航天液体动力全国重点实验室,陕西 西安 710100
National Key Laboratory of Aerospace Liquid Propulsion,Xi'an Aerospace Propulsion Institute, Xi'an 710100, China
centrifugal nozzle; long swirl cavity; gas injection atomization; breakage morphology; gas-liquid two-phase pressure building; atomization particle size
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9374.2024.03.004
注气雾化因在较低注气量下提高喷注器压降以获得较优的雾化效果[1-2],在气泡雾化[3-9]、壅塞雾化[10-12]及Y型喷嘴[13-16]等方面得到广泛应用。注气雾化主要通过“外气内液”或“外液内气”的喷嘴结构将稳定供应的气体注入液流中,从而在混合室与流道内形成预混的气液两相泡状流/段塞流/环状流/雾化环状流等[5]; 当气液两相流自喷嘴出口喷注而出时,气泡在流出喷孔前后经历加速、变形、膨胀和爆破等过程,伴随间歇性堵塞,一方面能够增强射流的破碎雾化[1, 17],另一方面易导致喷注雾化振荡[4, 8, 18]。
注气雾化过程中气液两相流通过喷孔后引起下游雾场中液滴浓度及速度波动[4, 8, 18],具有本质不稳定的特征。射流波动极易诱发燃烧振荡,导致启动压力峰和燃烧不稳定。当前所研究的注气雾化喷嘴的喷孔均为位于混合室底部的直流喷孔,喷注方向与来流方向一致,针对喷嘴结构参数、工况参数、气液两相流的流型与气泡尺寸对射流稳定性的影响规律进行了研究。对于结构参数的影响,研究表明:“外气内液”的注气喷嘴的射流雾化较为稳定[19]; 切向孔孔径越小数量越多、混合室长度越小,喷注雾化的振荡幅值越大[5, 9, 19-20],而注气角度的影响较小[18]; 喷嘴横向摆放时气液混合室内可能出现气液分层流动,导致喷注过程剧烈振荡[21]。对于工况参数的影响,随着注气量增加,喷注雾化的振荡频率降低[5]; 气液两相流型对射流不稳定程度的影响显著,相较于段塞流和环状流,泡状流产生的雾化射流较稳定[1, 7]。通过多孔介质[22]或数值模拟[8]控制气泡尺寸,研究表明:射流稳定性与气泡尺寸息息相关,气泡尺寸越大则射流越不稳定,当气泡尺寸与喷孔直径之比不大于1时射流较稳定[22]; 提高液体流速和气液质量流量比(gas-liquid ratio, GLR)有利于减小泡状流的气泡尺寸[8],当质量流量比不小于5%时不稳定程度较低,而当质量流量比不大于4%时不稳定程度持续波动[23]; 增加液体黏度有利于降低射流不稳定程度[18]。
研究者采用了高速摄影、激光多普勒测速仪(PDPA)、粒子成像测速仪(PIV)等光学测量方式定性或半定量衡量注气雾化过程的射流雾化不稳定性。基于高速摄影背光阴影拍摄的图像分析方法是最常用的定性衡量方式,高速摄影能够捕捉喷嘴内部混合室内的两相流动与喷嘴下游的雾化场,分析不同结构参数与工况参数作用下的两相流动流型与雾化场脉动特征[5, 8-9, 19-20, 24],利用POD(本征正交分解)等[7, 9]图像数据降维方法获得脉动特征幅值与频率,给出定性的影响规律。文献[25]结合电测量技术和高速摄像研究了内部流动参数(液体和气体的压力和体积流量)和流动状态对喷雾液滴平均直径的影响。文献[23]提出一种基于噪声信号的定性评估方法,利用自适应最优核算法处理噪声信息得到了喷雾声学的幅频分布。文献[26]利用PLIF(平面激光诱导荧光)和PIV技术测量雾化场瞬态质量流量以评估射流雾化的不稳定程度。文献[27]提出一种基于PDPA到达时间来定量衡量雾化液滴不稳定程度的方法,通过对比实际液滴与理想雾化模型中液滴达到测量点的时间间隔分布函数的偏差来判断稳定性。文献[4-5, 28]通过在混合室内壁面布置压力传感器来获得混合室内两相流振荡压力,分析混合室内的振荡与射流雾化脉动之间的相关性。
补燃循环液氧-煤油发动机预燃室的煤油喷嘴是一种旋流腔较长的敞口型离心喷嘴(长径比可能超过10,长径比为旋流腔长度与旋流腔直径的比值)。当液体火箭发动机启动阶段或在低工况工作时,离心喷嘴的喷注压降不足,直接影响燃料的雾化效果和点火启动,可能诱发发动机燃烧不稳定[4-5]。在不改变发动机喷嘴结构的基础上,采用氮气或氦气吹除发生器燃料头腔来提高喷注器压降[5, 29],改善煤油雾化效果,以保障发动机的平稳启动。另外,大范围变推力技术需要在低入口压力下实现多次可靠点火,同样采用氮气吹除乳化技术避免燃气发生器和推力室的喷注器压降过低,确保在大范围变工况下满足发动机高性能和高可靠性的要求[28-29]。离心式喷嘴广泛应用于液体火箭发动机,在较高压降时具有较好的雾化质量,但注气雾化易导致离心喷嘴的射流雾化不稳定。
本文所研究的注气雾化过程中,气体与液体在混合室内形成气液两相流,然后经离心喷嘴顶端的切向孔进入长旋流腔而发生破碎与雾化。与当前报道的传统气助雾化过程不同,首先,混合后的气液两相流通过切向孔后再进入长旋流腔,长旋流腔的摩擦造成动量矩损失,使喷嘴出口处的切向速度降低,气涡半径减小; 其次,切向孔使得射流方向与来流方向不一致,其节流作用削减了部分流体动量,提前发生气泡加速、变形、膨胀和爆破等过程,传统的气泡雾化喷嘴和气液离心喷嘴分析结论不再适用。因此,在尽量降低气体用量的前提下,为有效控制预燃室内煤油注气雾化的稳定性,有必要对长旋流腔敞口型离心喷嘴的注气雾化过程进行研究。本文以水和煤油模拟液作为液体工质,氮气和氦气作为气体工质,试验研究不同气体流量作用下的“外气内液”型长旋流腔敞口型离心喷嘴的雾化特性,为注气雾化推广应用提供规律认识。
试验系统如图1所示,主要包括气路供应系统、液路供应系统、测控系统与高速摄影拍摄装置。试验过程中针对不同的气体流量调整所用孔板,以保证孔板后压力在通液后保持稳定。管路内与工装内静压均通过压阻型静压传感器测得,各压力传感器安装位置见图1。气路与液路孔板前的压力传感器量程为0~10 MPa,精度为0.5级,混合室内压力传感器量程为0~2 MPa,精度为0.2级,各静压传感器的采样频率均为1 kHz。供应管路上设置质量流量计(艾默生Micro Motion F050),用于测量各工况的水流量(量程为0~30 g/s,精度为0.1级)与气体流量(量程为0~5 g/s,精度为0.1级)。试验中的各类传感器在试验前均通过检定。气液两相环状流射流出口的液膜破碎形态通过高速摄影获得。使用Phantom v2012型COMS黑白高速相机和LED面光源进行背光法雾化阴影图像拍摄,具体布置如图1所示。高速相机采样频率为20 kf/s(相邻两帧图像间的时间间隔为0.05 μs),拍摄图像为8位灰度图像,曝光时间为5 μs,图像分辨率为1 024×768像素,拍摄区域内每个像素表示约为0.01 mm×0.01 mm的区域。雾化粒径由DANTEC公司PDPA系统测量,具体布置形式与拍摄方法
参考文献[30]。
图1 长旋流腔敞口型离心喷嘴注气雾化试验系统
Fig.1 Experimental system of gas injection atomization for the open-end swirl injector with long swirl chamber
注气雾化试验喷嘴及其工装主要包括3部分:上部为气液混合部分; 中间为透明混合室; 下部为喷嘴试验件及其工装。气液混合为“外气内液”的混合方式,如图1所示,液体和气体分别通过顶部和侧面注入,其中气体流道轴线与混合室轴线的夹角为45°。喷嘴的顶部周向均布4个切向孔,气液两相流通过切向孔进入长旋流腔,最终在喷嘴出口射流、破碎与雾化,如图2所示。
图2 长旋流腔敞口型离心喷嘴注气雾化过程[5]
Fig.2 Gas injection atomization process of open-end swirl injector with long swirl chamber[5]
为获得瞬态启动过程参数,利用信号发生器同步采集压力传感器、流量计信号与高速摄影图像。试验时序如图3所示,t0为待喷嘴出口不再有残留液体排出时对应的时间。试验过程中首先开启数据采集系统,数采以1 kHz的频率记录系统各测点的压力与流量信号; 以信号发生器下降沿信号作为高速摄影拍摄的触发信号,同步记录雾化破碎图像与压力流量信号,并实现时序统一; 利用PDPA采集雾化粒径与速度时,将高速摄影替换为PDPA。编写了图像处理程序,并将压力与流量数据进行同步分析。
本文主要关心雾化形态、密度、黏度与表面张力等直接相关物性参数,其中表面张力尤为重要。如表1所示,比较煤油与水的物性参数,密度、表面张力与黏度对应的比值分别为1.2、3.04与0.53,表面张力差异最明显。考虑到使用煤油雾化具有一定的燃爆危险性,试验中配置煤油模拟液。相较于煤油,二者的密度相对偏差为4.65%; 黏度基本一致,相对偏差为2%; 表面张力略高,最大偏差为11.92%,基本满足当前注气雾化的试验要求。
未注气时喷嘴额定工况的压降Δpl=0.13 MPa,质量流量m·l=15.56 g/s,喷嘴的压降和流量均为测量周期内参数稳定后的平均值。利用高压气瓶出口的减压阀开度控制气体流量,注气量由0 g/s逐渐增加,获得不同的气液质量流量比。未注气时的喷注雾化如图4所示,旋流液膜在喷嘴出口未发生破碎,且在距离喷嘴出口一定距离内再次聚合,进一步在离心力与表面张力作用下破碎为液丝,液丝破碎为粒径较大的液滴。
图4 未注气时的喷注雾化图像(22 ms,m·l=15.56 g/s)
Fig.4 Image of spray atomization without gas injection(22 ms,m·l=15.56 g/s)
利用注气雾化高速摄影图像定性分析液膜破碎动态过程,初步分析注气量对液膜破碎形态和不稳定特性的影响规律。图5为不同注气流量时的注气离心喷嘴喷注液膜的破碎过程,液膜的破碎过程具有弱周期性(其中rgl为气液质量流量比)。根据破碎形态的差异,破碎过程可划分为3种不同的破碎模式,即爆裂型破碎[见图5(a)~图5(b)],多孔型破碎[见图5(c)]和轮缘型破碎[见图5(d)]。
图5 不同气液质量流量比时He/H2O喷注雾化形态
Fig.5 Atomization morphology of He/H2O injection at different gas-liquid ratios
当气体流量较大时,喷嘴出口处液膜直接在气动力作用下破碎为小液滴,呈现爆裂式破碎模式,如图5(a)~图5(b)所示。此时喷嘴旋流腔内的两相流为雾式环状流[5]。气液掺混较均匀,两相流在喷嘴出口受到气流剪切作用而破碎; 同时,外部压力减小而导致气泡膨胀破碎,从而出现显著的爆裂型破碎。从图5(a)~图5(b)可以观察到,在喷嘴下游中心区域存在间歇性的中心气流冲击,雾化液滴在气流冲击下发生二次破碎形成更小的雾化液滴,提升雾化液滴空间分布均匀性。分析认为,中心气流冲击的气体来自于泡状流经过切向孔时导致的相分离。随着注入气体的流量增大,中心气流的冲击频率提高,整体雾化场的均匀性提升,雾化液滴粒径减小。
保持液体流量不变,气体流量逐渐减小,喷嘴出口呈现间歇性喷注现象,即出现液膜主导或气体主导喷注。当液膜主导喷注时[见图5(c)],破碎距离较长,在膨胀拉长的过程中受到周围小液滴的撞击或者是由于自身湍流的作用,液膜上形成孔洞,如图6(a)所示,箭头所指为液膜孔洞。这些孔洞并不稳定,在表面张力作用下迅速扩大直至互相连接,形成网状液丝进而碎裂成为液滴。当气体主导喷注时,液膜在喷嘴出口处受气动力作用而直接破碎为小液滴,如图6(b)所示,在破碎液膜下方形成较大的液块。多孔型破碎也具有间歇性,形成液滴聚集的液滴群或大片未破碎的液块。
当气体流量进一步减小时,喷注液膜的破碎逐渐呈现轮缘型破碎[见图5(d)]。与图4喷嘴未注气时的喷注图像进行对比,在气流作用下,锥形液膜锥角增大,液膜破碎长度增长; 扩张液膜未发生收缩,而是呈现周向同时破裂的轮缘型破碎。破碎后的液膜在表面张力和中心气流的作用下形成粒径较大的液滴并径向扩散。随着液膜表面波的发展,在喷嘴下游液膜破碎具有明显的间歇性,形成典型的Klystron效应作用下的雾化液滴群,时间上具有周期性,空间上液滴群多层分布。
基于环状流射流中的气、液两相流动条件,对环状流射流液膜不同破碎模式下的动力学条件进行了分析,研究发现,环状流气液动量比α是影响液膜破碎模式的主要因素[31]。环状流射流气液动量比α定义为

式中:ρg和ρl分别为气相和液相密度; ug和ul分别为气流和液膜的流动速度。
入口折算速度ul(或ug)为质量流量m·l(或m·g)与切向孔截面积及液体(或气体)密度之比,密度采用20 ℃对应压力时的Refprop查询数值。
在环状流中,首先计算出环状流液膜的厚度,而后根据流量关系确定气流及液膜实际流通面积和实际流速。根据本实验工况条件和射流介质特征,采用Rizk等[32]关于旋流喷嘴内液膜厚度的关系式,即
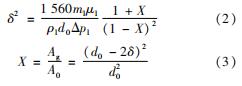
式中:d0为喷嘴出口管内径; δ为环状流液膜厚度; μl为液体黏度。
环状流液膜韦伯数Wel计算式为
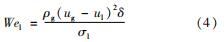
由于水与模拟液之间表面张力的差异明显,将二者的雾化破碎形态分别绘制于相图上,如图7所示。由图7可知:吹除水与模拟液的雾化形态在相图上区分明显,模拟液较低的表面张力导致较高的液膜韦伯数,相同的气液动量比时,能够获得更高的流体速度,液膜破碎更为剧烈; 吹除模拟液时,在较低的动量比下即进入爆裂型破碎,且多孔型破碎的分布范围较窄,说明较低的表面张力有助于注气雾化充分破碎为细小的液滴。
“外气内液”的离心式喷嘴注气雾化过程中伴随间歇性中心气流冲击,图8为He(吹除水)喷注雾化过程中的间歇性中心气流冲击发展过程。中心气流冲击后伴随大液块,在下游扩散形成离散液滴,直至下一次气流冲击。大液块的存在类似于Klystron效应作用下的液滴群分层分布,导致雾化场分布不均和释热集中,易引起燃烧不稳定。与此同时,当中心气流冲击发生时,喷嘴出口液膜在气流冲击作用下发生液滴二次破碎和强制掺混,获得更为均匀的雾化液滴分布和减小雾化粒径。因此,中心气流的冲击作用有助于雾化均匀和减小粒径,但气流冲击的时间间隙内易造成液滴分布不均,需要选择合适的气流流量使得冲击作用能够作用于下游分层液滴群,抑制或减轻注气雾化本身具有的雾化不稳定性。
不同气体流量时的气流冲击长度与发生间隔时间存在差异,如图9所示。随着气体流量减小,气流冲击长度减小,直至小于0.129 g/s气流冲击现象消失。气流冲击作用下的液滴二次破碎和强制掺混引起两方面影响:①冲击液团和大液滴,二次破碎后减小液滴尺寸,打破液滴群分层,使得雾化场更均匀; ②气流冲击引起液滴间碰撞聚并,使得下游气动力作用弱的区域液滴尺寸增大。在当前气体流量范围内,气体冲击是间歇发生的,发生时间间隔具有不确定性。因此,从雾化均匀性角度考虑:一是提高气液质量流量比,在气体剪切作用下将液膜破碎; 二是选择适中的气体流量,保证液膜在旋流作用下破碎为液滴,同时消除间歇性的气流冲击。综合考虑雾化均匀性与减少气体用量两方面,应选择合适的气体流量,在保证雾化均匀性的基础上,避免间歇性的气体冲击。
由于注气离心喷嘴内气液两相流工作过程本身具有一定的周期性脉动特性,为了获得全局平均结果,本文采用POD对连续拍摄的其中3 000张图像进行脉动模态分析,根据主要模态的主频及其对应的幅值来评估不同工作条件下的雾化脉动行为,反映喷注器对不同气体流量的响应特性。由图 10可知(图中色柱的绝对值表征图像上当前位置的像素相较于平均值的变化剧烈程度,正负为相位差异):对于爆裂型破碎,随着rgl由2.79%升高至3.85%,气流冲击的频率由48 Hz提高至87 Hz,云图中未出现明显的由液滴群聚集导致的分层现象; 对于多孔型破碎与轮缘型破碎,rgl由1.58%降至0.92%,云图中的雾化分层现象越来越明显,对应的雾化分层频率由19 Hz升至78 Hz。因此,气流冲击频率随rgl的变化是非线性的,当气流量较高或较低时,气流冲击频率都会升高,这一结果与文献[33]的分析结果一致。
图 10 不同rgl时He/H2O喷注雾化的第2阶POD模态及对应的FFT幅频特性
Fig.10 Frequency spectrums of the POD 2nd mode for the He/H2O injection at the different rgl
图 11中对比了两相混合建压稳定值随气体质量流量、气体体积流量和气体体积流量之比的变化。随着气体流量或气液体积流量比升高,混合室内的压力接近于线性增长。Casiano等[34]认为气体的加入使得小流量下的燃料具有更大的体积,从而提升了混合室内的压力。在相同的气体流量情况下,氦气注气雾化的两相建压稳定值明显高于氮气,且随着气体流量的增大,二者之间的差值逐步放大,两相建压稳定值之比(ph,He/ph,N2)逐渐增大且逐渐趋于定值[见图 12(a)],吹除水和模拟液时的ph,He/ph,N2分别稳定于2.7和3.0。混合室内达到相等的压力所需的氮气与氦气的质量流量之比(m·N2/m·He)随着稳定压力的升高而逐渐减小,直至趋近于定值[见图 12(b)],吹除水与模拟液时的m·N2/m·He分别稳定于3.45和4.00,即达到相同的喷注压降所需的氮气质量流量约为氦气的3.45倍(吹除水)与4倍(吹除模拟液)。对比氮气与氦气的气液体积流量比,可以看到氦气的气液体积流量比明显大于氮气[见图 12(c)]; 同样的两相混合建压稳定值,氦气的气液体积流量比基本为氮气的2倍(吹除水)与1.7倍(吹除模拟液)。
图 12 吹除水和模拟液时的两相建压稳定值变化
Fig.12 Variation on pressure of two-phase mixing for blow-off water and simulated liquid
为分析雾化形态与混合室内压力之间的关系,对试验过程中混合室内的压力进行FFT(快速傅里叶变换)分析,结果表明混合室内的压力不存在周期性的脉动特征。然而,氮气与氦气吹除作用时的压力波动幅值存在显著差异,氦气吹除时混合室内的压力波动幅值较大,可达到稳态压力的约10%,而氮气吹除时压力脉动较小,基本在稳定值的1%左右; 随着吹除气体流量增大,压力波动幅值增大。吹除水时的波动幅值大于吹除模拟液工况。
注气雾化试验过程中首先通气吹除以保证喷嘴出口不再出现液雾,然后开启液路气动阀通入液体。液体进入后压力快速上升。图 13为相同气体单独建压条件下对比氮气与氦气的两相建压速度,其中建压初期的压力上升速度基本一致,随后氮气工况的升高速度明显减缓,氦气的建压速度更快。定义v为建压速度,v=(pmix-pg)/tp表征液体通入后由单独气体建压到两相建压稳定值所用的时间,其中pmix为混合室内稳定压力的均值,pg为单独气体吹除时混合室内压力稳定值,充填时间tp为混合室内压力开始变化到压力达到稳定均值所需的时间。
图 13 单独气体建压相等时不同气体吹除作用下的建压过程及建压速度示意图
Fig.13 Pressure-building process with gases of N2 and He and schematic diagram of pressure-building velocity
图 14为两相建压速度随气体质量流量的变化。随着气体质量流量增大,建压速度逐渐加快,并逐渐趋近于定值,说明增大气体流量有助于快速建压,但建压速度存在上限。在当前试验参数范围内,吹除模拟液的氦气和氮气的最大建压速度分别为0.3 MPa/s与0.282 MPa/s,吹除水的氦气和氮气的最大建压速度分别为0.516 MPa/s与0.3 MPa/s。相同气体流量的条件下,氦气的建压速度明显高于氮气,分析原因主要为氦气密度较小,其与液体混合后的体积流量比明显大于氮气[见图 11(c)]。
总之,相同气体流量的条件下,氦气吹除能够获得更高的混合室内压力(喷注压降)和更快的建压速度,但两相混合建压过程中的压力波动更剧烈。
观察图5的液膜破碎形态,雾化液滴粒径随着吹除气量的增大而减小。为定量分析雾化液滴粒径的时空分布特性,利用PDPA测量雾化场中的10个位点,如图 15所示。
采用索特平均直径(Sauter mean diameter,SMD)d32作为雾化粒径的统计参数。观察图 16发现:首先随着气体单独建压的升高,雾化粒径逐渐减小,但单位气体单独建压增加引起的粒径减小量在降低; 其次,相同气体单独建压时,氦气吹除的雾化粒径普遍小于氮气; 再次,同一测量位点,氮气与氦气吹除水时的d32的变化趋势基本平行发展,意味两种气体作用下的质量流量存在比例关系,统计二者的拟合曲线,发现获得相同的雾化粒径时所需的气体质量流量总体符合m·N2/m·He=4.5的对应关系[见图 16(a)]。
图 16 雾化粒径d32随气体单独建压pg和气体质量流量的变化
Fig.16 Sauter mean diameter d32 varies with the gas pressure pg and the mass flow rate of gas
d32仅能反映总体平均值,无法反映粒径分布情况,如图 17所示,两工况的雾化粒径d32分别为197.5 μm与197.2 μm,基本一致; 但是两工况的雾化粒径分布明显不同,图 17(a)工况的峰值较小,粒径分布更为集中; 图 17(b)工况的峰值较高,粒径分布相对分散。因此,定义半峰全宽占比Nhalfheight/Nsum反映雾化粒径的相对分布,即半峰全宽(full width at half maximum, FWHM)范围内的粒数占总统计粒数的比例。将PDPA测量的雾化粒径柱状图采用核平滑密度函数进行拟合,获得连续的分布曲线,进而得到半峰全宽位置与拟合曲线的交点及其范围内的粒数。半峰全宽占比越高,则粒径分布越集中; 反之,分布越分散。
图 17 两工况雾化粒径d32接近时的半峰全宽占比
Fig.17 The full width at half maximum for two cases with the same d32
选取其中的4个测量位点,观察图 18可以发现大部分工况和位点处的半峰全宽占比随着气体质量流量增大而升高,即增加气体流量有助于雾化粒径均匀分布。但是,对于氦气吹除模拟液的工况,当气体流量高于0.3 g/s时,多个测量位点的Nhalfheight/Nsum发生明显的减小趋势,分析原因与图9中心气流间歇性冲击作用有关,气流冲击引起液滴间碰撞聚并,使得下游气动力作用弱的区域液滴尺寸增大,从而引起雾化粒径分布变得不均匀。
图 18 Nhalfheight/Nsum随气体质量流量的变化
Fig.18 Nhalfheight/Nsum varies with the mass flow rate of gas
本文针对长旋流腔敞口型离心喷嘴的注气雾化过程进行了试验研究,对喷注液膜破碎形态、气液两相混合建压与雾化粒径进行了量化分析,得到以下主要结论。
1)随着rgl升高,破碎模式逐步由轮缘型破碎、多孔型破碎过渡到爆裂型破碎; 同时,气流冲击的长度增大。但气流冲击频率随rgl的变化是非线性的,当气流量较高或较低时,气流冲击频率都会升高。
2)随着气体流量或气液体积流量比升高,混合室内的两相混合建压线性增长,建压速度加快,混合室内不存在周期性脉动,但不同气体吹除时的波动幅值存在显著差异。相同气体流量的条件下,氦气具有较快的建压速度和建压稳定值,但两相混合建压波动更为剧烈,ph,He/ph,N2稳定于2.7(吹除水)和3.0(吹除模拟液); 达到相等的两相建压所需的氮气量显著高于氦气,m·N2/m·He分别稳定于3.45(吹除水)和4.0(吹除模拟液)。氦气和氮气吹除时的混合室内压力波动幅值分别能达到稳态压力的10%与1%左右,随着吹除气体流量升高而增大。
3)提高气体流量有助于减小雾化粒径和均匀分布,在相同气体单独建压时,氦气吹除的雾化粒径普遍小于氮气。但当氦气吹除模拟液的气体流量过高(m·He>0.3 g/s)易引起气流冲击和液滴碰撞聚并,使得气动力作用弱的区域液滴尺寸增大,从而引起雾化粒径分布变得不均匀。