基金项目:中核集团青年英才项目; 中国科协青年托举人才工程
作者简介:周之帆(2001—),男,博士,研究领域为核热推进系统燃料组件流热力耦合仿真。
西安交通大学 核科学与技术学院,陕西 西安 710049
School of Nuclear Science Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
nuclear thermal propulsion; fuel element; thermal stress; fluid-structure interaction; safety analysis
核热推进概念诞生于20世纪40年代,作为一种大推力航天推进技术,其基本原理是利用核裂变反应产生的热量加热气体推进剂,获取火箭等宇宙飞行器的动力来源[1]。作为一种新式能源推进系统,核热推进系统具有比冲高、续航时间长、推力大、可多次启动等显著优势[2],有望突破传统化学推进的瓶颈,完成长距离的星际航行与空间探索任务[3-4],如今被认为是在深空探测领域最具前景的推进系统方案之一[5-6]。
20世纪50年代中期,美国与苏联已建立核热推进地面实验堆[7],针对核热推进技术,包括系统设计、燃料材料制备、运行实验与测试等方面突破多项关键技术,取得众多研究成果[8-9]。研究表明:在核热推进反应堆稳态运行工况中,堆芯内部燃料元件由于长期工作在高热流密度、大功率梯度、大温差、高温高速氢冷却剂冲刷的严苛服役条件下[10],核燃料基体材料内部的热应力集中现象严重[11],对堆芯燃料运行工况下的结构应力安全产生不利影响。为强化燃料元件的热工应力安全性能,燃料材料由初始的UO2一直发展到铀碳石墨基固溶体材料[7]、二元或三元碳化物材料[12]以及钨基/钼基金属陶瓷材料[13]等,但针对这些先进燃料的性能实验结果[12]与模拟计算结果[11]都表明燃料元件在运行过程中依旧可能出现涂层破裂、基体开裂或断裂等失效行为。
本研究针对核热推进反应堆在推进模式稳态运行期间堆芯冷却剂流动换热行为与燃料元件的热应力集中现象,对反应堆内部密排燃料组件典型基本单元建立对称模型,利用ANSYS Fluent与Abaqus联合仿真,开展燃料元件的流-热-力耦合计算分析,讨论反应堆运行时燃料元件的应力失效风险及影响因素,为核热推进系统的运行安全设计提供优化思路与参考依据。
核热推进反应堆堆芯组件的三维分析模型
参考文献[14]中的小型核火箭发动机(SNRE)反应堆,其对应的核热推进系统的工作原理如图1所示。系统内部的氢气工质闭式膨胀循环可以大体分为两部分:①液氢储罐中的氢被泵出后,首先沿喷管外壁流动以实现管壁的再生冷却,随后进入堆芯外部的反射层用以冷却控制鼓和反射层主体,最后这部分被预热的氢气进入涡轮机驱动泵; ②液氢工质被泵出后,进入堆芯中的连接管进行预热,由中心通道流入,边缘通道流出。最终,这两条支路的氢气工质汇合,进入堆芯冷却燃料元件,最后进入喷管实现喷气推进。
堆芯内的燃料组件包括燃料元件与连接管元件,其排布横截面如图2所示[15],其中燃料元件截面如图3所示。燃料总长0.89 m,基体材料为(U,Zr)C二元碳化物,内部通孔直径2.57 mm,各孔间距4.09 mm; 通孔内涂层材料为ZrC,厚度0.1 mm。图3中,支承燃料元件的连接管元件由利用不同材料制成的圆环与六棱柱基体相互嵌套构成,具体尺寸参数
参考文献[14]。
由于核热推进反应堆堆芯内部组件排布紧密,在反应堆运行过程中,燃料元件内部的热流分布情况可能会受连接管的冷却作用影响,在计算燃料温度分布时将连接管元件容纳入模拟模型中。由于燃料元件:连接管元件=2:1且其排布方式具有强对称性,在堆芯的基本阵列中截取“1/6燃料元件-1/12连接管元件”单元组件对,对整体组件模型进行简化处理,如图4所示,各截面的流-热-力边界均严格对称。
核热推进反应堆运行工况下,反应堆内的堆芯密排燃料组件温度分布受核燃料加热与高速氢气冷却的共同作用,而组件内危害运行安全的热应力集中分布现象是固体域特殊温度场的温度-应力耦合行为的力学响应,研究燃料组件的安全性能就是研究反应堆运行过程中堆芯整体流-热-力耦合问题[16]。针对这一复杂多场问题,参考小型核热火箭发动机设计的运行热工参数[14]与针对(U,Zr)C石墨基燃料材料的实验测试物性参数[12],植入高温氢气物性并引入能量与动量源项。建立了组件内冷却剂流动换热模型,利用ANSYS Fluent求解; 借助MpCCI多物理场耦合工具引入温度与压力参数,联合固体域导热方程以及应力应变增量关系式建立燃料元件热力耦合模型; 利用Abaqus求解,最终实现核热推进反应堆燃料元件流固耦合完整计算,具体分析流程如图5所示。
燃料元件与连接管元件内氢气的流动换热计算过程涉及连续性方程、动量方程及能量方程,其中湍流模型选用k-ω SST模型[17]。
质量守恒方程为
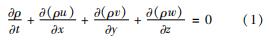
动量守恒方程为

能量守恒方程为
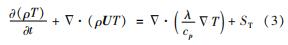
式中:p为作用在流体微元上的压力; Fi为流体微元所受体积力在三维方向的分量; τij为表面黏性应力沿空间三维方向的分量; λ为流体热导率; ST为黏性耗散项。
湍流模型中,湍流动能k的输运方程为[17]
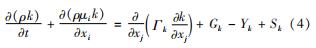
比耗散率ω的输运方程为
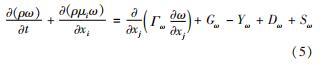
式中:Gk为湍流动能的生成项; Gω为比耗散率的生成项; Γk为湍流动能的有效扩散系数; Γω为比耗散率的有效扩散系数; Yk为湍流动能的耗散项; Yω为比耗散率的耗散项; Dω为交叉扩散系数; Sk为湍流动能的自定义源项; Sω为比耗散率的自定义源项。
关于固体域内的热传导,任意微元的热传导偏微分基本方程为
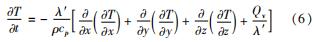
式中:λ'为固体热导率; Qv为热源功率密度。
在材料内部,温度分布不均将导致材料各部分热膨胀程度不同,从而导致材料各部分之间的相对形变产生热应力; 同时,材料随温度变化将发生韧脆转变现象,其弹塑性有所改变。对于弹性材料,其总应变为

弹性区内的应力应变增量关系为
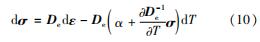
式中:dε为总应变增量; dεe为弹性应变增量; dεT为热应变增量; dσ为总应力增量; De为弹性应变增量矩阵; α为热膨胀系数。
对于塑性材料,其总应变增量为
dε=dεp+dεe+dεT(11)
塑性区内的应力应变增量关系为
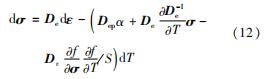
其中
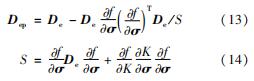
式中:dεp为塑性应变增量; Dep为塑性应变增量矩阵; f为材料的屈服函数; K为应变硬化指数。
由图1可知,系统内的氢气工质进入燃料元件时的热工状态受运行前半段氢气喷管壁再生回热与连接管内预热过程共同控制。由于本研究不涉及核热推进整体系统的构建,此处
参考文献[14,18]对350 MW小型核火箭发动机(SNRE)在推进模式下的堆芯冷却剂流动换热研究,选取本研究模型的运行参数,具体如表1所示[18]。燃料元件轴向功率密度分布关系
参考文献[19]针对该反应堆内(U,Zr)C二元碳化物燃料开发的MCNP输运模型计算结果,如图6所示,图中坐标轴z=0 m为燃料元件通道内的冷却剂出口。
表1 核热反应堆推进模式下各结构内流体初始边界参数
Tab.1 The initial fluid boundary parameters within each component under the nuclear-thermal propulsion mode
堆内燃料及连接管材料物性选用文献[12]针对(U,Zr)C二元碳化物燃料在NF-1测试堆中得到的实验测试物性数据,高温氢气模型选自西安交通大学韩梓超等人[20]研究的核热推进系统氢气物性模型。
对图4对应的简化模型进行结构化网格划分,网格模型如图7所示。利用上述计算条件进行网格无关性分析,结果如图8所示。以460万网格数模型作为误差计算基准,网格数高于80万后计算所得结果基本无变化,选定80万网格数模型进行后续分析计算。
选取Durham[18]在1972年针对小型核热火箭发动机开展的运行实验测试结果作为验证参考。实验结果与计算结果对比如表2所示,堆芯燃料元件冷却剂通道出口流体温度和压力与实验值的相对误差都在5%以内。
Stewart等[14]在2007年利用FLOTRAN程序对同类型核热推进反应堆的堆芯冷却剂流动换热行为进行了模拟,模拟过程所用计算条件与本研究一致。文献[14]中给出了燃料元件中心冷却剂通道距入口位置90%、70%、50%、30%、10%燃料全长处的流体温度与流速计算结果,与本文的计算结果进行对比,如图9所示。流体温度计算结果与文献参考值相差最大处位于距入口30%位置(z=0.623 m),计算值761.5 K,对比参考值709.2 K,相对偏差7.3%; 流体流速相差最大处位于距入口10%位置(z=0.801 m),计算值72.2 m/s,对比参考值68.5 m/s,相对偏差5.4%,结果符合要求。
对核热推进反应堆稳态运行工况进行模拟,具体运行参数与2.1节中保持一致。为准确说明堆芯冷却剂流动换热特性与燃料组件内部温度分布特点,对组件内各冷却剂子通道进行编号,如图 10所示。燃料元件冷却剂通道内部流体温度分布情况如图 11所示,各通道内冷却剂主流温度随燃料轴向位置分布情况如图 12所示,图中轴向z=0 m处为燃料元件内冷却剂出口位置。
图 12 各冷却剂通道内流体温度随轴向位置分布情况
Fig.12 Distribution of the coolant mainstream temperature with fuel axial position in each channel
模拟结果显示:燃料元件冷却剂平均出口温度约为2 600 K,流动过程中壁面流体最高温度可达2 870 K; 燃料元件中心冷却剂通道(C1)出口流体温度低于次中心通道(C2),更低于边缘通道(C3、C4、C5); 边缘通道中,越接近连接管一侧,内部出口流体温度越低。
燃料元件冷却剂入口压力为5.72 MPa且压力沿流动方向下降[21],考虑到压力数值较小且冷却剂通道在燃料元件内部平均分布,忽略流体壁面压力对燃料固体域应力分布的影响。
为确保核热推进反应堆稳态运行安全,燃料基体结构必须避免发生高温失效与结构断裂失效,针对燃料元件的温度-应力场耦合场分析是组件安全性能分析的研究重点。根据前文模拟所得燃料元件冷却剂通道壁面温度,结合燃料自身轴向功率密度分布,联合固体域导热方程求解,可以得出燃料元件内部温度场分布情况。
在核热反应堆稳态运行工况下,燃料元件的温度分布云图如图 13所示,燃料峰值温度为2 956 K,低于(U,Zr)C石墨基复合燃料元件的熔点3 000 K[12],排除高温失效风险。
燃料元件各冷却剂通道壁面的平均轴向温度分布情况如图 14所示,其中轴向位置z=0 m处为燃料元件内冷却剂出口位置。根据图 14中结果可知,燃料元件内各冷却剂通道壁面温度沿冷却剂流动方向先升高后降低,其温度极值落于燃料元件轴向z=0.15 m处附近。在该轴向位置截取横截面,观察燃料元件内部温度分布,结果如图 15所示。同一轴截面内,径向上,燃料元件内部温度由中心向边缘径向递减; 周向上,燃料元件温度极值分布于远离连接管一侧的燃料边缘位置。
根据堆芯结构传热设计可知,燃料元件内部温度分布受燃料自身释热、冷却剂流动换热与连接管导热共同作用。稳态运行工况下,燃料元件受自身冷却剂通道排布方式与连接管元件冷却作用影响导致内部热流分配不均,燃料元件边缘位置与中心位置最大温差超过350 K。燃料冷却剂通道周围不可能完全平均分配燃料体积,边缘通道附近的燃料元件相对体积占比更大,具体原理如图 16所示。图 15中燃料元件内部径向温度分布图上,靠近连接管元件一侧(C3)的燃料边缘温度明显低于远离连接管一侧的燃料边缘温度(C5),这说明堆芯中的连接管元件具有冷却燃料元件的作用,即可以影响燃料组件内部热流分配。
在设计燃料组件内部结构排布方式时,燃料元件与连接管元件之间预留了气隙。在不考虑工作过程中由于热膨胀产生的接触作用时,燃料元件内部的应力分布情况受以下因素控制:燃料元件温度分布情况和燃料元件在制作过程中被施加的预应力作用。
由于燃料元件内构成燃料基体的(U,Zr)C石墨基复合材料,其全温度下的热膨胀系数低于燃料涂层ZrC[22],因此在燃料元件升温膨胀过程中基体材料主要受拉应力作用,在判断燃料元件运行安全性能时主要考虑燃料基体的断裂与开裂失效风险。结合燃料元件内部温度分布情况,对固体域进行热力耦合分析,得到燃料基体第一主应力分布结果如图 17所示。结果显示:径向分布上,第一主应力主要集中于中心冷却剂通道附近,应力分布由中心向边缘径向递减; 轴向分布上,燃料元件内应力主要集中于结构中段接近冷却剂进口位置。
根据Luther[12]针对(U,Zr)C石墨复合材料的拉伸实验测试记录,燃料元件在全温度下的最低拉伸断裂应力为42 MPa,取该应力作为燃料基体的保守断裂失效强度。具体断裂强度随材料温度的变化情况见表3,表中相关数据通过分析文献[12]的实验数据得出。
根据保守化的燃料材料断裂失效强度标准,将燃料基体第一主应力云图中高于42 MPa区域标记为灰色,燃料基体应力失效风险区分布情况如图 18所示,其中图 18(a)为燃料基体整体应力分布情况,图 18(b)取燃料断裂失效风险区中心位置处(z=0.63 m)横截面。
图 18 稳态运行工况下燃料基体应力分布情况
Fig.18 Stress distribution in the fuel matrix under steady-state operating conditions
沿轴向取两处冷却剂通道壁面附近单元节点,对比各节点温度对应的实际抗拉强度最大拉应力,对比结果如图 19所示。结果表明,核热推进反应堆稳态运行工况下,燃料元件的C1和C2冷却剂通道壁面都存在断裂失效风险,且C2冷却剂通道壁面附近的燃料基体内部断裂失效风险相较于冷却剂通道C1更严重。
图 19 稳态运行工况下C1和C2壁面最大拉应力与抗拉强度对比
Fig.19 Comparison of maximum tensile stress and tensile strength of C1 and C2 walls
结合上述模拟计算结果,评估燃料元件在反应堆稳态运行工况下的安全性能后可以确定:堆芯燃料元件在工作时存在断裂失效风险,风险形成原因是燃料基体在中心冷却剂通道附近存在最大拉应力高于实际抗拉强度的结构区域。
根据热应力产生条件,分析燃料元件温度分布与应力分布,可知其内部应力集中现象的形成机制:燃料元件径向温差带来的热膨胀差异在轴向上的积累,导致燃料边缘对中心产生轴向拉伸。如图 20所示,在反应堆运行至稳态工况时,由于燃料元件的边缘温度高于中心温度,燃料的中心区域膨胀程度较低而边缘膨胀程度较高,燃料元件中心-边缘的相对形变造成边缘区域带动中心拉伸、中心区域限制边缘膨胀的现象,形成燃料中心的拉应力集中现象。
这一机理说明,要缓解燃料元件内的热应力集中,其本质就是要平衡燃料元件内部的温度分配,降低燃料元件中心-边缘的相对温差。因此在燃料元件设计方面,可以考虑通过调整燃料元件各冷却剂通道内的涂层厚度或对部分通道进行节流处理,以在合理范围内增大边缘通道冷却剂流量,加速对燃料边缘部分的冷却,降低燃料内部的径向温差,相关方法在文献[11]中也有所提及。适当降低燃料元件的稳态运行输出功率同样被视为一种可用手段,在保持燃料元件各流体边界输入不变的情况下,调整稳态运行功率为原功率的95%,计算结果显示燃料元件内部的最大主应力由原先的50.3 MPa下降至45.5 MPa,且应力集中现象得到明显缓解,如图 21所示。但考虑到核热推进整体系统中燃料元件的冷却剂进口热工参数还受喷管壁再生回热影响,降低运行功率后喷管位置的温度也将随之下降,在实际过程中,通过降低运行功率来改善燃料结构的热工应力这一方法的可行性需要结合系统进行综合分析。
本研究联合利用ANSYS Fluent和Abaqus等模拟计算软件,基于已有的核热推进反应堆设计、流量、功率等条件,对堆内燃料元件及冷却剂的流-热-应力耦合场进行模拟计算,分析燃料运行安全性,评估(U,Zr)C石墨基燃料基体材料的开裂与断裂失效风险。根据分析结果,可以得到以下结论。
1)燃料元件冷却剂出口平均温度约2 600 K,不同位置冷却剂通道内部氢冷却剂出口温度存在差异,由于边缘通道附近的燃料元件相对体积占比更高,总体上边缘通道内冷却剂温度高于中心通道。
2)燃料元件无高温熔融风险,但结构内部存在较大温差; 受冷却剂通道排布方式以及连接管的冷却作用影响,燃料元件中心温度低于燃料边缘温度,最大温差可达350 K左右。
3)燃料元件内部温差引发燃料基体材料中段的拉应力集中现象,第一主应力峰值达到50 MPa,高于材料抗拉强度,存在燃料基体断裂失效风险; 应力集中现象的形成原因是燃料元件径向温差带来的热膨胀差异在轴向上的积累。